Amoxicillin or tetracycline in bismuth-containing quadruple therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection
- PMID: 32362221
- PMCID: PMC7524369
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1754118
Amoxicillin or tetracycline in bismuth-containing quadruple therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
Aim: To compare the efficacy and safety between modified quadruple- and bismuth-containing quadruple therapy as first-line eradication regimen for Helicobacter pylori infection.
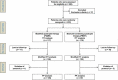
Methods: This study was a multicenter, randomized-controlled, non-inferiority trial. Subjects endoscopically diagnosed with H. pylori infection were randomly allocated to receive modified quadruple- (rabeprazole 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1 g bid, metronidazole 500 mg tid, bismuth subcitrate 300 mg qid [elemental bismuth 480 mg]; PAMB) or bismuth-containing quadruple therapy (rabeprazole 20 mg bid, bismuth subcitrate 300 mg qid, metronidazole 500 mg tid, tetracycline 500 mg qid; PBMT) for 14 days. Rates of eradication success and adverse events were investigated. Antibiotic resistance was determined using the agar dilution and DNA sequencing of the clarithromycin resistance point mutations in the 23 S rRNA gene of H. pylori.
Results: In total, 233 participants were randomized, 27 were lost to follow-up, and four violated the protocol. Both regimens showed an acceptable eradication rate in the intention-to-treat (PAMB: 87.2% vs. PBMT: 82.8%, P = .37), modified intention-to-treat (96.2% vs. 96%, P > .99), and per-protocol (96.2% vs. 96.9%, P > .99) analyses. Non-inferiority in the eradication success between PAMB and PBMT was confirmed. The amoxicillin-, metronidazole-, tetracycline-, clarithromycin-, and levofloxacin-resistance rates were 8.3, 40, 9.4, 23.5, and 42.2%, respectively. Antimicrobial resistance did not significantly affect the efficacy of either therapy. Overall compliance was 98.1%. Adverse events were not significantly different between the two therapies.
Conclusion: Modified quadruple therapy comprising rabeprazole, amoxicillin, metronidazole, and bismuth is an effective first-line treatment for the H. pylori infection in regions with high clarithromycin and metronidazole resistance.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; bismuth; disease eradication; drug resistance; metronidazole.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial Shows that both 14-Day Hybrid and Bismuth Quadruple Therapies Cure Most Patients with Helicobacter pylori Infection in Populations with Moderate Antibiotic Resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Oct 24;61(11):e00140-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00140-17. Print 2017 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28807915 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Modified quadruple therapy versus bismuth-containing quadruple therapy in first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in Korea; rationale and design of an open-label, multicenter, randomized controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(46):e13245. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013245. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30431605 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of sequential therapy and amoxicillin/tetracycline containing bismuth quadruple therapy for the first-line eradication of Helicobacter pylori: a prospective, multi-center, randomized clinical trial.BMC Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul 26;16(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0490-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27460100 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Second-line rescue treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: Where are we now?World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Oct 28;24(40):4548-4553. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4548. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30386104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new look at anti-Helicobacter pylori therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep 21;17(35):3971-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i35.3971. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22046084 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy comparison of 7- and 14-day P-CAB based bismuth-containing quadruple regimen with PPI based bismuth-containing quadruple regimen for Helicobacter pylori infection: rationale and design of an open-label, multicenter, randomized controlled trial.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Dec 21;23(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-03100-y. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 38129806 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: From potential biomolecular mechanisms to clinical practice.J Clin Lab Anal. 2023 Apr;37(7):e24885. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24885. Epub 2023 Apr 23. J Clin Lab Anal. 2023. PMID: 37088871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cure rate of 10-day bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication is equivalent to 14-day: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Aug;23(4):1033-1043. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00953-7. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36538198
-
Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Resistance in Patients Enrolled in Guangzhou, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Aug 3;16:5033-5038. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S418482. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37554543 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023 Apr 20;9(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00431-8. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023. PMID: 37081005 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain CA, Gisbert JP, Kuipers EJ, Axon AT, Bazzoli F, Gasbarrini A, Atherton J, Graham DY, et al. Management of helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence consensus report. Gut. 2017;66:6–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical