Understanding the binding affinity of noscapines with protease of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19 using MD simulations at different temperatures
- PMID: 32362235
- PMCID: PMC7212547
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1752310
Understanding the binding affinity of noscapines with protease of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19 using MD simulations at different temperatures
Abstract
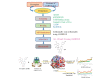
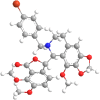
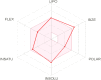
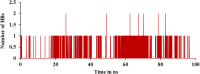
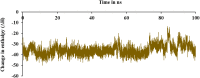
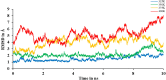
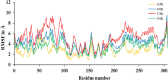
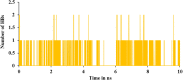
The current outbreak of a novel coronavirus, named as SARS-CoV-2 causing COVID-19 occurred in 2019, is in dire need of finding potential therapeutic agents. Recently, ongoing viral epidemic due to coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) primarily affected mainland China that now threatened to spread to populations in most countries of the world. In spite of this, there is currently no antiviral drug/ vaccine available against coronavirus infection, COVID-19. In the present study, computer-aided drug design-based screening to find out promising inhibitors against the coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) leads to infection, COVID-19. The lead therapeutic molecule was investigated through docking and molecular dynamics simulations. In this, binding affinity of noscapines(23B)-protease of SARS-CoV-2 complex was evaluated through MD simulations at different temperatures. Our research group has established that noscapine is a chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of drug resistant cancers; however, noscapine was also being used as anti-malarial, anti-stroke and cough-suppressant. This study suggests for the first time that noscapine exerts its antiviral effects by inhibiting viral protein synthesis.
Keywords: COVID-19; MD simulations; Protease of SARS-CoV-2; molecular docking; noscapine; screening.
Figures








References
-
- Aaboud M., & ATLAS Collaboration. (2017). Determination of the strong coupling constant alpha s from transverse energy-energy correlations in multijet events at s = 8 TeV using the ATLAS detector. The European Physical Journal C, 77(12), 872, 1-34. doi. 10.1140/epjc/s10052-017-5442-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aaboud M., ATLAS Collaboration, Aad G., Abbott B., Abdinov O., Abeloos B., Abhayasinghe D. K., Abidi S. H., AbouZeid O. S., Abraham N. L., Abramowicz H., Abreu H., Abulaiti Y., Acharya B. S., Adachi S., Adamczyk L., Adelman J., Adersberger M., Adiguzel A., … Zwalinski L. (2018). Probing the quantum interference between Singly and Doubly resonant top-quark production in pp collisions at sqrt[s] = 13 TeV with the ATLAS Detector. Physical Review Letters, 121(15), 152002. - PubMed
-
- Abbad A., Perera R. A., Anga L., Faouzi A., Minh N. N. T., Malik S. M. M. R., Iounes N., Maaroufi A., Van Kerkhove M. D., Peiris M., & Nourlil J. (2019). Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) neutralising antibodies in a high-risk human population, Morocco, November 2017 to January 2018. Eurosurveillance, 24(48), 1900244 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.48.1900244 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adasme-Carreno F., Munoz-Gutierrez C., Caballero J., & Alzate-Morales J. H. (2014). Performance of the MM/GBSA scoring using a binding site hydrogen bond network-based frame selection: The protein kinase case. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 16(27), 14047–14055. 10.1039/C4CP01378F - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
