Antibiotics alone as an alternative to appendectomy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults: Changes in treatment modalities related to the COVID-19 health crisis
- PMID: 32362368
- PMCID: PMC7181971
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2020.04.014
Antibiotics alone as an alternative to appendectomy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults: Changes in treatment modalities related to the COVID-19 health crisis
Abstract
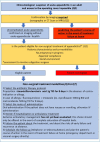
The massive inflow of patients with COVID-19 requiring urgent care has overloaded hospitals in France and impacts the management of other patients. Deferring hospitalization and non-urgent surgeries has become a priority for surgeons today in order to relieve the health care system. It is obviously not simple to reduce emergency surgery without altering the quality of care or leading to a loss of chance for the patient. Acute appendicitis is a very specific situation and the prevalence of this disease leads us to reconsider this particular disease in the context of the COVID-19 crisis. Indeed, while the currently recommended treatment for uncomplicated acute appendicitis is surgical appendectomy, the non-surgical alternative of medical management by antibiotic therapy alone has been widely evaluated by high-quality studies in the literature. Insofar as the main limitation of exclusively medical treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis is the risk of recurrent appendicitis, this treatment option represents an alternative of choice to reduce the intra-hospital overload in this context of health crisis. The aim of this work is therefore to provide physicians and surgeons with a practical guide based on a review of the literature on the medical treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults, to offer this alternative treatment to the right patients and under good conditions, especially when access to the operating room is limited or impossible.
Keywords: Acute appendicitis; Antibiotic therapy; Appendectomy; COVID-19; Coronavirus.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.
Figures
References
-
- Vons C., Brami M. Épidémiologie descriptive des appendicites en France : faut-il revoir la physiopathologie des appendicites aiguës ? Bull Acad Natle Med. 2017;201(1–2–3):339–357. [séance du 14 février 2017]
-
- Eriksson S., Granström L. Randomized controlled trial of appendicectomy versus antibiotic therapy for acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 1995;82:166–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical