Rabbit Clinical Pathology
- PMID: 32362792
- PMCID: PMC7185592
- DOI: 10.1053/j.jepm.2007.06.002
Rabbit Clinical Pathology
Abstract
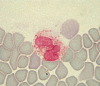
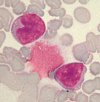
With rabbit patients, as in other species, analyzing blood and urine samples can be useful and informative, although interpretation of the results is sometimes challenging. This article summarizes the interpretation of laboratory results from rabbits. Hematological parameters can yield information about the red blood cell population and leukocyte response to stress and pathogens. Biochemistry evaluation can be used to investigate liver, kidney, and other organ function, and urinalysis results may yield additional information about kidney function and electrolyte imbalances. Serological tests are available for several pathogens of rabbits, including Encephalitozoon cuniculi, although the significance of positive results and antibody titers is not clear. Serum protein electrophoresis aids the understanding of protein disorders and the immune response to acute and chronic inflammation.
Keywords: biochemistry; blood sampling; hematology; rabbit; serum protein electrophoresis; urinalysis.
Copyright © 2007 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Harcourt-Brown F.M., Baker S.J. Parathyroid hormone, hematological and biochemical parameters in relation to dental disease and husbandry in pet rabbits. J Small Anim Pract. 2001;42:130–136. - PubMed
-
- Fudge A.M. Rabbit hematology. In: Fudge A.M., editor. Laboratory Medicine: Avian and Exotic Pets. WB Saunders Company; Philadelphia, PA: 2000. pp. 273–275.
-
- Saunders R.A., Davies R.R. Blackwell Publishing; Oxford, UK: 2005. Notes on Rabbit Internal Medicine.
-
- Weisbroth S.H. Neoplastic diseases. In: Manning P.J., Ringler D.H., Newcomer C.E., editors. The Biology of Laboratory Rabbit. (ed 2) Academic Press; New York, NY: 1994. pp. 259–292.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
