Composite Monte Carlo decision making under high uncertainty of novel coronavirus epidemic using hybridized deep learning and fuzzy rule induction
- PMID: 32362799
- PMCID: PMC7195106
- DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106282
Composite Monte Carlo decision making under high uncertainty of novel coronavirus epidemic using hybridized deep learning and fuzzy rule induction
Abstract
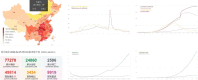
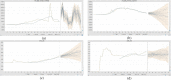
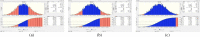
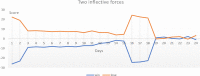
In the advent of the novel coronavirus epidemic since December 2019, governments and authorities have been struggling to make critical decisions under high uncertainty at their best efforts. In computer science, this represents a typical problem of machine learning over incomplete or limited data in early epidemic Composite Monte-Carlo (CMC) simulation is a forecasting method which extrapolates available data which are broken down from multiple correlated/casual micro-data sources into many possible future outcomes by drawing random samples from some probability distributions. For instance, the overall trend and propagation of the infested cases in China are influenced by the temporal-spatial data of the nearby cities around the Wuhan city (where the virus is originated from), in terms of the population density, travel mobility, medical resources such as hospital beds and the timeliness of quarantine control in each city etc. Hence a CMC is reliable only up to the closeness of the underlying statistical distribution of a CMC, that is supposed to represent the behaviour of the future events, and the correctness of the composite data relationships. In this paper, a case study of using CMC that is enhanced by deep learning network and fuzzy rule induction for gaining better stochastic insights about the epidemic development is experimented. Instead of applying simplistic and uniform assumptions for a MC which is a common practice, a deep learning-based CMC is used in conjunction of fuzzy rule induction techniques. As a result, decision makers are benefited from a better fitted MC outputs complemented by min-max rules that foretell about the extreme ranges of future possibilities with respect to the epidemic.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; COVID-19; Coronavirus; Decision support; Monte Carlo simulation.
© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- CDC . 2016. Outbreaks chronology: Ebola virus disease. January 20. (Accessed 22 January 2016)
-
- The World Bank . 2014. GDP Growth (annual %) external. (Accessed 20 January 2016)
-
- Feuer W. NBC Universal; 2020. Coronavirus: The Hit To the Global Economy Will Be Worse than SARS. Feb 6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
