The Variety in the Common Theme of Translation Inhibition by Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems
- PMID: 32362907
- PMCID: PMC7180214
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00262
The Variety in the Common Theme of Translation Inhibition by Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems
Abstract
Type II Toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules are bacterial operons that encode a toxic protein and its antidote, which form a self-regulating genetic system. Antitoxins put a halter on toxins in many ways that distinguish different types of TA modules. In type II TA modules, toxin and antitoxin are proteins that form a complex which physically sequesters the toxin, thereby preventing its toxic activity. Type II toxins inhibit various cellular processes, however, the translation process appears to be their favorite target and nearly every step of this complex process is inhibited by type II toxins. The structural features, enzymatic activities and target specificities of the different toxin families are discussed. Finally, this review emphasizes that the structural folds presented by these toxins are not restricted to type II TA toxins or to one particular cellular target, and discusses why so many of them evolved to target translation as well as the recent developments regarding the role(s) of these systems in bacterial physiology and evolution.
Keywords: mobile genetic elements; persistence; programmed cell death; toxins; translation.
Copyright © 2020 Jurėnas and Van Melderen.
Figures

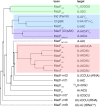
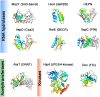

Similar articles
-
Novel toxins from type II toxin-antitoxin systems with acetyltransferase activity.Plasmid. 2017 Sep;93:30-35. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Plasmid. 2017. PMID: 28941941 Review.
-
Toxin-antitoxin systems as multilevel interaction systems.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Jan 10;6(1):304-24. doi: 10.3390/toxins6010304. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24434905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial type II toxin-antitoxin systems acting through post-translational modifications.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Dec 11;19:86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.12.002. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33384857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keeping the Wolves at Bay: Antitoxins of Prokaryotic Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems.Front Mol Biosci. 2016 Mar 22;3:9. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00009. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27047942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxin-antitoxin systems and their medical applications: current status and future perspective.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;105(5):1803-1821. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11134-z. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33582835 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Potential for Cross-Interactions of Antitoxins in Type II TA Systems.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jun 26;12(6):422. doi: 10.3390/toxins12060422. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32604745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type II bacterial toxin-antitoxins: hypotheses, facts, and the newfound plethora of the PezAT system.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023 Sep 5;47(5):fuad052. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad052. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37715317 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic Small Alarmone Synthetase FaRel2 inhibits translation by pyrophosphorylating tRNAGly and tRNAThr.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 5:2024.07.05.602228. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.05.602228. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2024 Nov 15;10(46):eadr9624. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adr9624. PMID: 39005314 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
HEPN RNases - an emerging class of functionally distinct RNA processing and degradation enzymes.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Feb;56(1):88-108. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2020.1856769. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33349060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of the Streptococcus pneumoniae Toxin-Antitoxin RelBE Proteins with Their Target DNA.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 15;9(4):851. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040851. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33921033 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

