Manipulating angiotensin metabolism with angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in heart failure
- PMID: 32362932
- PMCID: PMC7185729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ddstr.2013.11.001
Manipulating angiotensin metabolism with angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in heart failure
Abstract
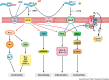
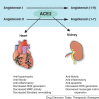
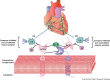
Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), is a monocarboxypeptidase which metabolizes several peptides including the degradation of Ang II, a peptide with vasoconstrictive/proliferative/effects, to generate Ang 1-7, which acting through its receptor Mas exerts vasodilatory/anti-proliferative actions. The classical pathway of the RAS involving the ACE-Ang II-AT1 receptor axis is antagonized by the second arm constituted by the ACE2-Ang 1-7/Mas receptor axis. Loss of ACE2 enhances the adverse pathological remodeling susceptibility to pressure-overload and myocardial infarction. Human recombinant ACE2 is also a negative regulator of Ang II-induced myocardial hypertrophy, fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction and suppresses pressure-overload induced heart failure. Due to its characteristics, the ACE2-Ang 1-7/Mas axis may represent new possibilities for developing novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of heart failure. Human recombinant ACE2 has been safely administered to healthy human volunteers intravenously resulting in sustained lowering of plasma Ang II levels. In this review, we will summarize the beneficial effects of ACE2 in heart disease and the potential use of human recombinant ACE2 as a novel therapy for heart failure.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Zaman M.A. Drugs targeting the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002;1:621–636. - PubMed
-
- Bader M., Ganten D. Update on tissue renin–angiotensin systems. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2008;86:615–621. - PubMed
-
- Donoghue M. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ. Res. 2000;87:E1–E9. - PubMed
-
- Tipnis S.R. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:33238–33243. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
