Epidemiology of community acquired pneumonia
- PMID: 32362935
- PMCID: PMC7185481
- DOI: 10.1016/j.paed.2012.05.002
Epidemiology of community acquired pneumonia
Abstract
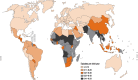
Despite efforts in prevention worldwide including recent advances in vaccine therapy, childhood community acquired pneumonia (CAP) remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality both in the developed and the developing world. Traditionally, qualifying the aetiology of CAP proved to be fraught with challenges particularly due to low yields from blood and sputum specimens. In recent years however, new advances in techniques such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and polymerase chain reaction have dramatically improved detection rates of both bacteria and viruses. In addition to qualifying the true burden of disease by known organisms such as Streptococcus pneumoniae it has led to the identification of organisms such as human bocavirus which have not previously been associated with CAP. This article aims to provide a brief update to the clinician on the current epidemiology of CAP in this post-vaccination era. It is based on a combination of recommendations from existing clinical practice guidelines, recent systematic reviews and the current literature.
Keywords: children; community acquired pneumonia; epidemiology; guidelines; infection; prevalence.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Garenne M., Ronsmans C., Campbell H. The magnitude of mortality from acute respiratory infections in children under 5 years in developing countries. World Health Stat Q. 1992;45:180–191. - PubMed
-
- Gentile A., Bardach A., Ciapponi A. Epidemiology of community-acquired pneumonia in children of Latin America and the Caribbean: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2012;16:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Harris M., Clark J., Coote N. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in children: update 2011. Thorax. 2011;66:927–928. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous