Spontaneous Remission in a Patient With Acute Myeloid Leukemia Leading to Undetectable Minimal Residual Disease
- PMID: 32362981
- PMCID: PMC7188378
- DOI: 10.14740/jh606
Spontaneous Remission in a Patient With Acute Myeloid Leukemia Leading to Undetectable Minimal Residual Disease
Abstract
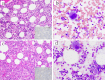
Although rare, spontaneous remission (SR) of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has been reported in the literature, the underlying mechanisms driving remission remain unknown. However, it is most commonly associated with a preceding severe infection. We present a case of a 40-year-old man with no past medical history who presented to our hospital with severe left hip pain and fevers and was found to have AML. Chemotherapy was delayed because the patient required extensive debridement and fasciotomy of his left hip and a prolonged course of antibiotics. After his acute illness had stabilized, a repeat bone marrow biopsy was performed which showed no abnormal myeloid blasts and resolution of his original cytogenetic and molecular abnormalities. At the time of this writing, our patient remains in remission with undetectable minimal residual disease (MRD), now 14 months from his initial diagnosis of AML.
Keywords: AML; Minimal residual disease; Spontaneous remission.
Copyright 2020, Helbig et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Eisenlohr C. Leucaemia lienalis, lymphatica et medullaris mit multiplen Gehirnnervenlahmungen. Archiv fur Pathologie, Anatomie und Physiologie und fur Klinische Medizin. 1878;73:56–73. doi: 10.1007/BF01994747. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
