A Term Neonatal Case With Lethal Respiratory Failure Associated With a Novel Homozygous Mutation in ABCA3 Gene
- PMID: 32363169
- PMCID: PMC7181334
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.00138
A Term Neonatal Case With Lethal Respiratory Failure Associated With a Novel Homozygous Mutation in ABCA3 Gene
Abstract
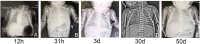
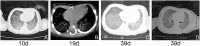
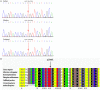
The mutations in the ABCA3 (ATP-binding cassette transporter subfamily A member 3) gene could result in lethal respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) in neonates and interstitial lung disease (ILD) in infants and children. Here, we describe a full-term newborn who manifested respiratory distress 20 min after birth and then gradually developed hypoxemic respiratory failure and died on 53 days of life. A homozygous missense mutation (c.746C >T) was identified in exon 8 of ABCA3 gene in the neonate by next-generation sequencing, and the mutations were inherited from parents, respectively. This homozygous mutation is the first reported to date.
Keywords: ABCA3 gene; full-term neonate; interstitial lung diseases; lethal respiratory distress syndrome; pulmonary surfactant.
Copyright © 2020 Wei, Fu, Han and Ma.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

