MRI follow-up after magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound for non-invasive thalamotomy: the neuroradiologist's perspective
- PMID: 32363482
- PMCID: PMC7410861
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-020-02433-9
MRI follow-up after magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound for non-invasive thalamotomy: the neuroradiologist's perspective
Abstract
Purpose: Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS) systems are increasingly used to non-invasively treat tremor; consensus on imaging follow-up is poor in these patients. This study aims to elucidate how MRgFUS lesions evolve for a radiological readership with regard to clinical outcome.
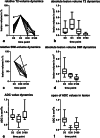
Methods: MRgFUS-induced lesions and oedema were retrospectively evaluated based on DWI, SWI, T2-weighted and T1-weighted 3-T MRI data acquired 30 min and 3, 30 and 180 days after MRgFUS (n = 9 essential tremor, n = 1 Parkinson's patients). Lesions were assessed volumetrically, visually and by ADC measurements and compared with clinical effects using non-parametric testing.
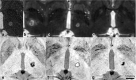
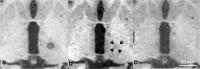
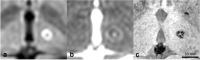
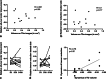
Results: Thirty minutes after treatment, all lesions could be identified on T2-weighted images. Immediate oedema was rare (n = 1). Lesion volume as well as oedema reached a maximum on day 3 with a mean lesion size of 0.4 ± 0.2 cm3 and an oedema volume 3.7 ± 1.2 times the lesion volume. On day 3, a distinct diffusion-restricted rim was noted that corresponded well with SWI. Lesion shrinkage after day 3 was observed in all sequences. Lesions were no longer detectable on DWI in n = 7/10, on T2-weighted images in n = 4/10 and on T1-weighted images in n = 4/10 on day 180. No infarcts or haemorrhage were observed. There was no correlation between lesion size and initial motor skill improvement (p = 0.99). Tremor reduction dynamics correlated strongly with lesion shrinkage between days 3 and 180 (p = 0.01, R = 0.76).
Conclusion: In conclusion, cerebral MRgFUS lesions variably shrink over months. SWI is the sequence of choice to identify lesions after 6 months. Lesion volume is arguably associated with intermediate-term outcome.
Keywords: Essential tremor; High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation; Magnetic resonance imaging; Parkinson disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wintermark M, Druzgal J, Huss DS, Khaled MA, Monteith S, Raghavan P, Huerta T, Schweickert LC, Burkholder B, Loomba JJ, Zadicario E, Qiao Y, Shah B, Snell J, Eames M, Frysinger R, Kassell N, Elias WJ. Imaging findings in MR imaging-guided focused ultrasound treatment for patients with essential tremor. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;35(5):891–896. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3808. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elias WJ, Lipsman N, Ondo WG, Ghanouni P, Kim YG, Lee W, Schwartz M, Hynynen K, Lozano AM, Shah BB, Huss D, Dallapiazza RF, Gwinn R, Witt J, Ro S, Eisenberg HM, Fishman PS, Gandhi D, Halpern CH, Chuang R, Butts Pauly K, Tierney TS, Hayes MT, Cosgrove GR, Yamaguchi T, Abe K, Taira T, Chang JW. A randomized trial of focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(8):730–739. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1600159. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

