COX-2-PGE2-EPs in gynecological cancers
- PMID: 32363546
- PMCID: PMC7246249
- DOI: 10.1007/s00404-020-05559-6
COX-2-PGE2-EPs in gynecological cancers
Abstract
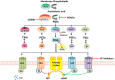
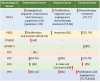
Purpose: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and selective COX-2 inhibitors (COXibs) inhibit the progression of endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer and cervical cancer. However, concerning the adverse effects of NSAIDs and COXibs, it is still urgent and necessary to explore novel and specific anti-inflammation targets for potential chemoprevention. The signaling of cyclooxygenase 2-prostaglandin E2-prostaglandin E2 receptors (COX-2-PGE2-EPs) is the central inflammatory pathway involved in the gynecological carcinogenesis.
Methods: Literature searches were performed to the function of COX-2-PGE2-EPs in gynecological malignancies.
Results: This review provides an overview of the current knowledge of COX-2-PGE2-EPs signaling in endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer and cervical cancer. Many studies demonstrated the upregulated expression of the whole signaling pathway in gynecological malignancies and some focused on the function of COX-2 and cAMP-linked EP2/EP4 and EP3 signaling pathway in gynecological cancer. By contrast, roles of EP1 and the exact pathological mechanisms have not been completely clarified. The studies concerning EP receptors in gynecological cancers highlight the potential advantage of combining COX enzyme inhibitors with EP receptor antagonists as therapeutic agents in gynecological cancers.
Conclusion: EPs represent promising anti-inflammation biomarkers for gynecological cancer and may be novel treatment targets in the near future.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2); Endometrial cancer; Ovarian cancer; Prostaglandin E2 receptors (EPs).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dossus L, Rinaldi S, Becker S, Lukanova A, Tjonneland A, Olsen A, Stegger J, Overvad K, Chabbert-Buffet N, Jimenez-Corona A, Clavel-Chapelon F, Rohrmann S, Teucher B, Boeing H, Schutze M, Trichopoulou A, Benetou V, Lagiou P, Palli D, Berrino F, Panico S, Tumino R, Sacerdote C, Redondo ML, Travier N, Sanchez MJ, Altzibar JM, Chirlaque MD, Ardanaz E, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, van Duijnhoven FJ, Onland-Moret NC, Peeters PH, Hallmans G, Lundin E, Khaw KT, Wareham N, Allen N, Key TJ, Slimani N, Hainaut P, Romaguera D, Norat T, Riboli E, Kaaks R. Obesity, inflammatory markers, and endometrial cancer risk: a prospective case-control study. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17(4):1007–1019. doi: 10.1677/ERC-10-0053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coleman RA, Smith WL, Narumiya S. International Union of Pharmacology classification of prostanoid receptors: properties, distribution, and structure of the receptors and their subtypes. Pharmacol Rev. 1994;46(2):205–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

