Feline sporotrichosis in Asia
- PMID: 32363567
- PMCID: PMC7966660
- DOI: 10.1007/s42770-020-00274-5
Feline sporotrichosis in Asia
Abstract
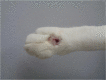
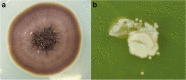
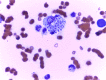
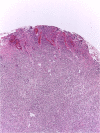
Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato is currently recognized as a species complex with only Sporothrix brasiliensis, Sporothrix schenckii sensu stricto, Sporothrix globosa and Sporothrix pallida identified to cause disease in the cat. Feline sporotrichosis in Asia is mainly reported from Malaysia where a single clonal strain of clinical clade D, Sporothrix schenckii sensu stricto manifesting low susceptibility to major antifungal classes, has been identified as the agent of the disease. Sporothrix globosa has been identified to cause disease from a single cat in Japan while the specific species of agent has not been identified yet for the disease in Thailand. Despite efforts to elucidate and describe the pathogenicity of the agent and the disease it causes, the paucity of data highlights the need for further molecular epidemiological studies to characterize this fungus and the disease it causes in Asia. Its prognosis remains guarded to poor due to issues pertaining to cost, protracted treatment course, zoonotic potential and low susceptibility of some strains to antifungals.
Keywords: Asia; Feline sporotrichosis; Malaysia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Zhou X, Rodrigues A, Feng P, Hoog GS. Global ITS diversity in the Sporothrix schenckii complex. Fungal Divers. 2013;2013:1–13.
-
- Han HS, Kano R, Chen C, Noli C. Comparisons of two in vitro antifungal sensitivity tests and monitoring during therapy of Sporothrix schenckii sensu stricto in Malaysian cats. Vet Dermatol. 2017;28:156–e32. - PubMed
-
- Kano R, Tsui CKM, Hamelin RC, Anzawa K, Mochizuki T, Nishimoto K, Hiruma M, Kamata H, Hasegawa A. The MAT1-1:MAT1-2 ratio of Sporothrix globosa isolates in Japan. Mycopathologia. 2015;179:81–86. - PubMed
-
- Schubach TMP, Menezes RC, Wanke B. Sporotrichosis. In: Greene CE, editor. Infectious diseases of the dog and cat. 4. St. Louis: Saunders Elsevier; 2012. pp. 645–650.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

