Sex Differences in Symptom Presentation in Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 32363989
- PMCID: PMC7428564
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014733
Sex Differences in Symptom Presentation in Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
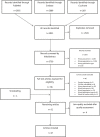
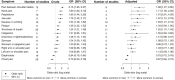
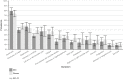
Background Timely recognition of patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is important for successful treatment. Previous research has suggested that women with ACS present with different symptoms compared with men. This review assessed the extent of sex differences in symptom presentation in patients with confirmed ACS. Methods and Results A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane up to June 2019. Two reviewers independently screened title-abstracts and full-texts according to predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Methodological quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Pooled odds ratios (OR) with 95% CI of a symptom being present were calculated using aggregated and cumulative meta-analyses as well as sex-specific pooled prevalences for each symptom. Twenty-seven studies were included. Compared with men, women with ACS had higher odds of presenting with pain between the shoulder blades (OR 2.15; 95% CI, 1.95-2.37), nausea or vomiting (OR 1.64; 95% CI, 1.48-1.82) and shortness of breath (OR 1.34; 95% CI, 1.21-1.48). Women had lower odds of presenting with chest pain (OR 0.70; 95% CI, 0.63-0.78) and diaphoresis (OR 0.84; 95% CI, 0.76-0.94). Both sexes presented most often with chest pain (pooled prevalences, men 79%; 95% CI, 72-85, pooled prevalences, women 74%; 95% CI, 72-85). Other symptoms also showed substantial overlap in prevalence. The presence of sex differences has been established since the early 2000s. Newer studies did not materially change cumulative findings. Conclusions Women with ACS do have different symptoms at presentation than men with ACS, but there is also considerable overlap. Since these differences have been shown for years, symptoms should no longer be labeled as "atypical" or "typical."
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; diagnosis; meta‐analysis; sex differences; symptoms; systematic review.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sensitivity, specificity, and sex differences in symptoms reported on the 13-item acute coronary syndrome checklist.J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Apr 2;3(2):e000586. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000586. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24695650 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing sensitivity and specificity of the Manchester Triage System in the evaluation of acute coronary syndrome in adult patients in emergency care: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Nov;13(11):64-73. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2213. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26657465
-
Relations of Sex to Diagnosis and Outcomes in Acute Coronary Syndrome.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Mar 10;7(6):e007297. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007297. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29525782 Free PMC article.
-
Time to standardize and broaden the criteria of acute coronary syndrome symptom presentations in women.Can J Cardiol. 2014 Jul;30(7):721-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2013.10.015. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Can J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24530216 Review.
-
Symptom presentation of women with acute coronary syndromes: myth vs reality.Arch Intern Med. 2007 Dec 10;167(22):2405-13. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.22.2405. Arch Intern Med. 2007. PMID: 18071161 Review.
Cited by
-
Symptom recognition and treatment-seeking behaviors in women experiencing acute coronary syndrome for the first time: a qualitative study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Nov 28;22(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02892-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 36443668 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the management and outcome of acute coronary syndrome-Still an issue of equal treatment?Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2023 Dec;135(23-24):663-666. doi: 10.1007/s00508-023-02302-4. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2023. PMID: 37994938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual Dimorphism in Cardiovascular Biomarkers: Clinical and Research Implications.Circ Res. 2022 Feb 18;130(4):578-592. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319916. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35175850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Why We Need a Stronger Focus on Women's Health in Clinical Psychology and Psychological Treatment.Clin Psychol Eur. 2024 Sep 30;6(3):e15683. doi: 10.32872/cpe.15683. eCollection 2024 Sep. Clin Psychol Eur. 2024. PMID: 39678315 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Gender and Social Inequalities in Awareness of Coronary Artery Disease in European Countries.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jan 26;19(3):1388. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19031388. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35162415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roth GA, Johnson C, Abajobir A, Abd‐Allah F, Abera SF, Abyu G, Ahmed M, Aksut B, Alam T, Alam K, Alla F, Alvis‐Guzman N, Amrock S, Ansari H, Ärnlöv J, Asayesh H, Atey TM, Avila‐Burgos L, Awasthi A, Banerjee A, Barac A, Bärnighausen T, Barregard L, Bedi N, Belay Ketema E, Bennett D, Berhe G, Bhutta Z, Bitew S, Carapetis J, Carrero JJ, Malta DC, Castañeda‐Orjuela CA, Castillo‐Rivas J, Catalá‐López F, Choi JY, Christensen H, Cirillo M, Cooper L Jr, Criqui M, Cundiff D, Damasceno A, Dandona L, Dandona R, Davletov K, Dharmaratne S, Dorairaj P, Dubey M, Ehrenkranz R, El Sayed Zaki M, Faraon EJA, Esteghamati A, Farid T, Farvid M, Feigin V, Ding EL, Fowkes G, Gebrehiwot T, Gillum R, Gold A, Gona P, Gupta R, Habtewold TD, Hafezi‐Nejad N, Hailu T, Hailu GB, Hankey G, Hassen HY, Abate KH, Havmoeller R, Hay SI, Horino M, Hotez PJ, Jacobsen K, James S, Javanbakht M, Jeemon P, John D, Jonas J, Kalkonde Y, Karimkhani C, Kasaeian A, Khader Y, Khan A, Khang YH, Khera S, Khoja AT, Khubchandani J, Kim D, Kolte D, Kosen S, Krohn KJ, Kumar GA, Kwan GF, Lal DK, Larsson A, Linn S, Lopez A, Lotufo PA, El Razek HMA, Malekzadeh R, Mazidi M, Meier T, Meles KG, Mensah G, Meretoja A, Mezgebe H, Miller T, Mirrakhimov E, Mohammed S, Moran AE, Musa KI, Narula J, Neal B, Ngalesoni F, Nguyen G, Obermeyer CM, Owolabi M, Patton G, Pedro J, Qato D, Qorbani M, Rahimi K, Rai RK, Rawaf S, Ribeiro A, Safiri S, Salomon JA, Santos I, Santric Milicevic M, Sartorius B, Schutte A, Sepanlou S, Shaikh MA, Shin MJ, Shishehbor M, Shore H, Silva DAS, Sobngwi E, Stranges S, Swaminathan S, Tabarés‐Seisdedos R, Tadele Atnafu N, Tesfay F, Thakur JS, Thrift A, Topor‐Madry R, Truelsen T, Tyrovolas S, Ukwaja KN, Uthman O, Vasankari T, Vlassov V, Vollset SE, Wakayo T, Watkins D, Weintraub R, Werdecker A, Westerman R, Wiysonge CS, Wolfe C, Workicho A, Xu G, Yano Y, Yip P, Yonemoto N, Younis M, Yu C, Vos T, Naghavi M, Murray C. Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:1–25. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Global Health Estimates 2016: Deaths by cause, age, sex, by country and by region, 2000–2016. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
-
- An L, Li W, Shi H, Zhou X, Liu X, Wang H, Liu J, Fan S. Gender difference of symptoms of acute coronary syndrome among Chinese patients: a cross‐sectional study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2019;18:179–184. - PubMed
-
- Koopman C, Vaartjes I, Heintjes EM, Spiering W, van Dis I, Herings RMC, Bots ML. Persisting gender differences and attenuating age differences in cardiovascular drug use for prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease, 1998–2010. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:3198–3205. - PubMed
-
- Johansson I, Strömberg A, Swahn E. Factors related to delay times in patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction. Heart Lung. 2004;33:291–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

