Hybrid Coils-Based Wireless Power Transfer for Intelligent Sensors
- PMID: 32365800
- PMCID: PMC7248994
- DOI: 10.3390/s20092549
Hybrid Coils-Based Wireless Power Transfer for Intelligent Sensors
Abstract
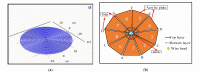
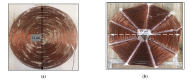
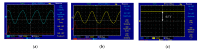
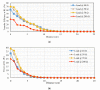
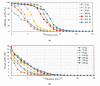
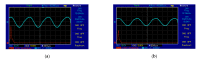
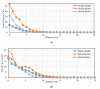
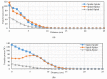
Most wearable intelligent biomedical sensors are battery-powered. The batteries are large and relatively heavy, adding to the volume of wearable sensors, especially when implanted. In addition, the batteries have limited capacity, requiring periodic charging, as well as a limited life, requiring potentially invasive replacement. This paper aims to design and implement a prototype energy harvesting technique based on wireless power transfer/magnetic resonator coupling (WPT/MRC) to overcome the battery power problem by supplying adequate power for a heart rate sensor. We optimized transfer power and efficiency at different distances between transmitter and receiver coils. The proposed MRC consists of three units: power, measurement, and monitoring. The power unit included transmitter and receiver coils. The measurement unit consisted of an Arduino Nano microcontroller, a heart rate sensor, and used the nRF24L01 wireless protocol. The experimental monitoring unit was supported by a laptop to monitor the heart rate measurement in real-time. Three coil topologies: spiral-spiral, spider-spider, and spiral-spider were implemented for testing. These topologies were examined to explore which would be the best for the application by providing the highest transfer power and efficiency. The spiral-spider topology achieved the highest transfer power and efficiency with 10 W at 87%, respectively over a 5 cm air gap between transmitter and receiver coils when a 200 Ω resistive load was considered. Whereas, the spider-spider topology accomplished 7 W and 93% transfer power and efficiency at the same airgap and resistive load. The proposed topologies were superior to previous studies in terms of transfer power, efficiency and distance.
Keywords: arduino; heart rate sensor; nRF24L01; transfer efficiency; transfer power.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures















References
-
- Mahmood M.F., Mohammed S.L., Gharghan S.K. Energy Harvesting-Based Vibration Sensor for Medical Electromyography Device. Int. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. Telecommun. 2020;9 doi: 10.18178/ijeetc.OJS-19209X. - DOI
-
- Shaw T., Mitra D. Metasurface-based radiative near-field wireless power transfer system for implantable medical devices. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2019;13:1974–1982. doi: 10.1049/iet-map.2019.0141. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

