Looking at Fog Computing for E-Health through the Lens of Deployment Challenges and Applications
- PMID: 32365815
- PMCID: PMC7248890
- DOI: 10.3390/s20092553
Looking at Fog Computing for E-Health through the Lens of Deployment Challenges and Applications
Abstract
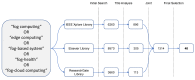
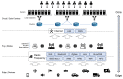
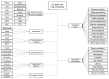
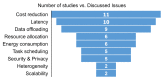
Fog computing is a distributed infrastructure where specific resources are managed at the network border using cloud computing principles and technologies. In contrast to traditional cloud computing, fog computing supports latency-sensitive applications with less energy consumption and a reduced amount of data traffic. A fog device is placed at the network border, allowing data collection and processing to be physically close to their end-users. This characteristic is essential for applications that can benefit from improved latency and response time. In particular, in the e-Health field, many solutions rely on real-time data to monitor environments, patients, and/or medical staff, aiming at improving processes and safety. Therefore, fog computing can play an important role in such environments, providing a low latency infrastructure. The main goal of the current research is to present fog computing strategies focused on electronic-Health (e-Health) applications. To the best of our knowledge, this article is the first to propose a review in the scope of applications and challenges of e-Health fog computing. We introduce some of the available e-Health solutions in the literature that focus on latency, security, privacy, energy efficiency, and resource management techniques. Additionally, we discuss communication protocols and technologies, detailing both in an architectural overview from the edge devices up to the cloud. Differently from traditional cloud computing, the fog concept demonstrates better performance in terms of time-sensitive requirements and network data traffic. Finally, based on the evaluation of the current technologies for e-Health, open research issues and challenges are identified, and further research directions are proposed.
Keywords: Internet of Things; cloud computing; e-health; fog computing; healthcare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bonomi F., Milito R., Natarajan P., Zhu J. Big Data and Internet of Things: A Roadmap for Smart Environments. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2014. Fog computing: A platform for internet of things and analytics; pp. 169–186.
-
- Arunkumar G., Venkataraman N. A novel approach to address interoperability concern in cloud computing. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015;50:554–559. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2015.04.083. - DOI
-
- Atlam H.F., Alenezi A., Alharthi A., Walters R.J., Wills G.B. Integration of cloud computing with internet of things: Challenges and open issues; Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData); Exeter, UK. 21–23 June 2017; pp. 670–675.
-
- Stojmenovic I., Wen S. The fog computing paradigm: Scenarios and security issues; Proceedings of the 2014 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS); Warsaw, Poland. 7–10 September 2014; pp. 1–8.
-
- Bonomi F., Milito R., Zhu J., Addepalli S. Fog computing and its role in the internet of things; Proceedings of the First Edition of the MCC Workshop on Mobile Cloud Computing; Helsinki, Finland. 17 August 2012; New York, NY, USA: ACM; 2012. pp. 13–16.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

