circNFIB1 inhibits lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis via the miR-486-5p/PIK3R1/VEGF-C axis in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 32366257
- PMCID: PMC7197141
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01205-6
circNFIB1 inhibits lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis via the miR-486-5p/PIK3R1/VEGF-C axis in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Patients with lymph node (LN)-positive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) have extremely poor survival rates. Circular RNAs (circRNAs), a newly discovered type of endogenous noncoding RNAs, have been proposed to mediate the progression of diverse types of tumors. However, the role and underlying regulatory mechanisms of circRNAs in the LN metastasis of PDAC remain unknown.
Methods: Next-generation sequencing was used to identify differentially expressed circRNAs between PDAC and normal adjacent tissues. In vitro and in vivo experiments were conducted to evaluate the functional role of circNFIB1. RNA pulldown and luciferase assays were performed to examine the binding of circNFIB1 and miR-486-5p.
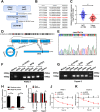
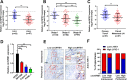
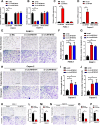
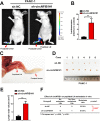
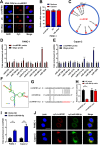
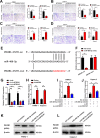
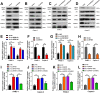
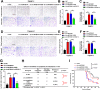
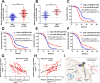
Results: In the present study, we identified that a novel circRNA (circNFIB1, hsa_circ_0086375) was downregulated in PDAC and negatively associated with LN metastasis in PDAC patients. Functionally, circNFIB1 knockdown promoted lymphangiogenesis and LN metastasis of PDAC both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, circNFIB1 functioned as a sponge of miR-486-5p, and partially reversed the effect of miR-486-5p. Moreover, circNFIB1 attenuated the oncogenic effect of miR-486-5p and consequently upregulated PIK3R1 expression, which further downregulated VEGF-C expression through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway, and ultimately suppressed lymphangiogenesis and LN metastasis in PDAC.
Conclusions: Our findings provide novel insight into the underlying mechanism of circRNA-mediated LN metastasis of PDAC and suggest that circNFIB1 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for LN metastasis in PDAC.
Keywords: Lymphatic metastasis; PI3K/Akt signaling pathway; PIK3R1; Pancreatic cancer; circNFIB1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Philip PA, Mooney M, Jaffe D, Eckhardt G, Moore M, Meropol N, Emens L, O'Reilly E, Korc M, Ellis L, et al. Consensus report of the national cancer institute clinical trials planning meeting on pancreas cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5660–5669. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.21.9022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Groot VP, Gemenetzis G, Blair AB, Rivero-Soto RJ, Yu J, Javed AA, Burkhart RA, Rinkes I, Molenaar IQ, Cameron JL, et al. Defining and predicting early recurrence in 957 patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 2019;269:1154–1162. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002734. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

