Pre-transplant MRD negativity predicts favorable outcomes of CAR-T therapy followed by haploidentical HSCT for relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a multi-center retrospective study
- PMID: 32366260
- PMCID: PMC7199358
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-00873-7
Pre-transplant MRD negativity predicts favorable outcomes of CAR-T therapy followed by haploidentical HSCT for relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a multi-center retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Consolidative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is a controversial option for patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia after chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy. We performed a multicenter retrospective study to assess whether patients can benefit from haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after CAR-T therapy.
Methods: A total of 122 patients after CAR-T therapy were enrolled, including 67 patients without subsequent transplantation (non-transplant group) and 55 patients with subsequent haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (transplant group). Long-term outcome was assessed, as was its association with baseline patient characteristics.
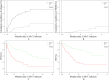
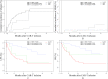
Results: Compared with the non-transplant group, transplantation recipients had a higher 2-year overall survival (OS; 77.0% versus 36.4%; P < 0.001) and leukemia-free survival (LFS; 65.6% versus 32.8%; P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that minimal residual disease (MRD) positivity at transplantation is an independent factor associated with poor LFS (P = 0.005), OS (P = 0.035), and high cumulative incidence rate of relapse (P = 0.045). Pre-transplant MRD-negative recipients (MRD- group) had a lower cumulative incidence of relapse (17.3%) than those in the non-transplant group (67.2%; P < 0.001) and pre-transplant MRD-positive recipients (MRD+ group) (65.8%; P = 0.006). The cumulative incidence of relapse in MRD+ and non-transplant groups did not differ significantly (P = 0.139). The 2-year LFS in the non-transplant, MRD+, and MRD- groups was 32.8%, 27.6%, and 76.1%, respectively. The MRD- group had a higher LFS than the non-transplantation group (P < 0.001) and MRD+ group (P = 0.007), whereas the LFS in the MRD+ and non-transplant groups did not differ significantly (P = 0.305). The 2-year OS of the MRD- group was higher than that of the non-transplant group (83.3% versus 36.4%; P < 0.001) but did not differ from that of the MRD+ group (83.3% versus 62.7%; P = 0.069). The OS in the non-transplant and MRD+ groups did not differ significantly (P = 0.231).
Conclusion: Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with pre-transplant MRD negativity after CAR-T therapy could greatly improve LFS and OS in patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Trial registration: The study was registered in the Chinese clinical trial registry (ChiCTR1900023957).
Keywords: Chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy; Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Leukemia-free survival; Minimal residual disease negativity; Overall survival; Relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Gökbuget N, Stanze D, Beck J, Diedrich H, Horst HA, Hüttmann A, et al. Outcome of relapsed adult lymphoblastic leukemia depends on response to salvage chemotherapy, prognostic factors, and performance of stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120:2032–2041. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-399287. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

