FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation
- PMID: 32367036
- PMCID: PMC7316630
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-0669-6
FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation
Abstract
Cytosolic sensing of pathogens and damage by myeloid and barrier epithelial cells assembles large complexes called inflammasomes, which activate inflammatory caspases to process cytokines (IL-1β) and gasdermin D (GSDMD). Cleaved GSDMD forms membrane pores, leading to cytokine release and inflammatory cell death (pyroptosis). Inhibiting GSDMD is an attractive strategy to curb inflammation. Here we identify disulfiram, a drug for treating alcohol addiction, as an inhibitor of pore formation by GSDMD but not other members of the GSDM family. Disulfiram blocks pyroptosis and cytokine release in cells and lipopolysaccharide-induced septic death in mice. At nanomolar concentration, disulfiram covalently modifies human/mouse Cys191/Cys192 in GSDMD to block pore formation. Disulfiram still allows IL-1β and GSDMD processing, but abrogates pore formation, thereby preventing IL-1β release and pyroptosis. The role of disulfiram in inhibiting GSDMD provides new therapeutic indications for repurposing this safe drug to counteract inflammation, which contributes to many human diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

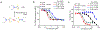




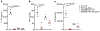
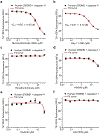



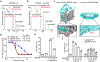


Comment in
-
Jack of all trades inhibits inflammation (in sober people).Nat Immunol. 2020 Jul;21(7):718-719. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0693-6. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32577009 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lamkanfi M & Dixit VM Inflammasomes and their roles in health and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28, 137–161 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Broz P & Dixit VM Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 16, 407–420 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Kayagaki N et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 526, 666–671 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Shi J et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 526, 660–665 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

