Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 32367037
- PMCID: PMC8135909
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-0677-6
Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
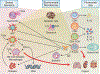
Impressive progress has been made over the last several years toward understanding how almost every aspect of the immune system contributes to the expression of systemic autoimmunity. In parallel, studies have shed light on the mechanisms that contribute to organ inflammation and damage. New approaches that address the complicated interaction between genetic variants, epigenetic processes, sex and the environment promise to enlighten the multitude of pathways that lead to what is clinically defined as systemic lupus erythematosus. It is expected that each patient owns a unique 'interactome', which will dictate specific treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Durcan L, O’Dwyer T & Petri M Management strategies and future directions for systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. Lancet 393, 2332–2343 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Dörner T & Furie R Novel paradigms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 393, 2344–2358 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Tsokos GC Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 2110–2121 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Deng Y & Tsao BP Updates in lupus genetics. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 19, 68 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

