Effects of Mu-Opiate Receptor Gene Polymorphism rs1799971 (A118G) on the Antidepressant and Dissociation Responses in Esketamine Nasal Spray Clinical Trials
- PMID: 32367114
- PMCID: PMC7710914
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa030
Effects of Mu-Opiate Receptor Gene Polymorphism rs1799971 (A118G) on the Antidepressant and Dissociation Responses in Esketamine Nasal Spray Clinical Trials
Abstract
Background: At ketamine and esketamine doses at which antidepressant doses are achieved, these agents are relatively selective, noncompetitive, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists. However, at substantially higher doses, ketamine has shown mu-opioid receptor (MOR-gene symbol: OPRM1) agonist effects. Preliminary clinical studies showed conflicting results on whether naltrexone, a MOR antagonist, blocks the antidepressant action of ketamine. We examined drug-induced or endogenous MOR involvement in the antidepressant and dissociative responses to esketamine by assessing the effects of a functional single nucleotide polymorphism rs1799971 (A118G) of OPRM1, which is known to alter MOR agonist-mediated responses.
Methods: Participants with treatment-resistant depression from 2 phase III, double-blind, controlled trials of esketamine (or placebo) nasal spray plus an oral antidepressant were genotyped for rs1799971. Participants received the experimental agents twice weekly for 4 weeks. Antidepressant responses were rated using the change in Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) score on days 2 and 28 post-dose initiation, and dissociative side effects were assessed using the Clinician-Administered Dissociative-States Scale at 40 minutes post-dose on days 1 and 25.
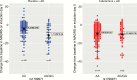
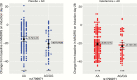
Results: In the esketamine + antidepressant arm, no significant genotype effect of single nucleotide polymorphism rs1799971 (A118G) on MADRS score reductions was detected on either day 2 or 28. By contrast, in the antidepressant + placebo arm, there was a significant genotype effect on MADRS score reductions on day 2 and a nonsignificant trend on day 28 towards an improvement in depression symptoms in G-allele carriers. No significant genotype effects on dissociative responses were detected.
Conclusions: Variation in rs1799971 (A118G) did not affect the antidepressant response to esketamine + antidepressant. Antidepressant response to antidepressant + placebo was increased in G-allele carriers, compatible with previous reports that release of endorphins/enkephalins may play a role in mediating placebo effect.
Trial registration: NCT02417064 and NCT02418585; www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Keywords: depression; esketamine; ketamine; mu-opioid receptor; polymorphism.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures
References
-
- Aalto S, Ihalainen J, Hirvonen J, Kajander J, Scheinin H, Tanila H, Någren K, Vilkman H, Gustafsson LL, Syvälahti E, Hietala J (2005) Cortical glutamate-dopamine interaction and ketamine-induced psychotic symptoms in man. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 182:375–383. - PubMed
-
- Aslaksen PM, Forsberg JT, Gjerstad J (2018) The opioid receptor mu 1 (OPRM1) rs1799971 and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) rs4680 as genetic markers for placebo analgesia. Pain 159:2585–2592. - PubMed
-
- Bond C, LaForge KS, Tian M, Melia D, Zhang S, Borg L, Gong J, Schluger J, Strong JA, Leal SM, Tischfield JA, Kreek MJ, Yu L (1998) Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human mu opioid receptor gene alters beta-endorphin binding and activity: possible implications for opiate addiction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:9608–9613. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

