[Use of health information on the internet: personal and motivational influencing factors]
- PMID: 32367207
- PMCID: PMC8516774
- DOI: 10.1007/s00103-020-03144-5
[Use of health information on the internet: personal and motivational influencing factors]
Erratum in
-
Erratum zu: Nutzung von Gesundheitsinformationen im Internet: personenbezogene und motivationale Einflussfaktoren.Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2022 Mar;65(3):396. doi: 10.1007/s00103-021-03447-1. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2022. PMID: 34698888 Free PMC article. German. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and objectives: Taking an active role in healthcare requires comprehensive health knowledge. One's own online search for health information can contribute to an appropriate information base. Therefore, it seems essential to determine the extent to which online services and health apps are currently used in Germany as well as to analyze which personal and motivational factors influence whether and how often the German public search for health information online or use health apps.
Methods: We conducted an online survey among the German public in a sample stratified by demographic characteristics (N = 3000). The questionnaire measured the health-related use of the Internet and health apps as well as possible personal and motivational factors. The relevance of these factors for explaining the Internet use for health-related purposes was determined by regression analyses.
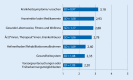
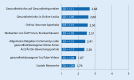
Results: While health-related information searches using the Internet are widespread in Germany, health apps are used less frequently. In particular health information platforms are most frequently used to search for information on disease symptoms. Turning to the Internet for health-related purposes is mainly influenced by motivational factors. Having current health problems and possessing information-seeking skills are particularly influential factors for an individual's Internet use.
Conclusions: In order to unfold the potential associated with health-related online information-seeking behaviors, it is necessary that people are motivated and feel competent to gather online information themselves. In particular, the corresponding skills need to be promoted in order to reduce the risk of increasing informational, health, and social disparities.
Zusammenfassung: HINTERGRUND UND ZIELE: Die Übernahme einer aktiven Patient*innen-Rolle kann nur auf einer entsprechenden Informationsgrundlage gelingen. Die eigene Suche nach Gesundheitsinformationen im Internet kann zu einer solchen adäquaten Wissensbasis beitragen. Daher erscheint es zentral zu fragen, was die derzeitige Nutzung von Onlineangeboten und Gesundheits-Apps in Deutschland auszeichnet und welche personenbezogenen und motivationalen Einflussfaktoren beeinflussen, ob und wie häufig die Bürger*innen online nach Gesundheitsinformationen suchen oder Gesundheits-Apps nutzen.
Methoden: Zur Beantwortung der Fragestellungen wurde eine an der deutschen Gesamtbevölkerung stratifizierte Onlinebefragung (N = 3000) durchgeführt. Der Fragebogen erfasste die gesundheitsbezogene Nutzung des Internets und von Apps sowie mögliche personenbezogene und motivationale Einflussfaktoren. Die Bedeutung dieser Faktoren für die Internetnutzung wurde mittels Regressionsanalysen ermittelt.
Ergebnisse: Die gesundheitsbezogene Informationssuche mittels Internet ist in Deutschland weitverbreitet, während Gesundheits-Apps noch deutlich seltener genutzt werden. Am häufigsten werden auf Gesundheitsportalen Informationen zu Krankheitssymptomen gesucht. Die Zuwendung zum Internet wird besonders durch motivationale Faktoren geprägt. Akute Betroffenheit von körperlichen Beschwerden und entsprechende Informationskompetenzen sind die einflussreichsten Faktoren für die Internetnutzung.
Diskussion: Um die mit der Informationssuche im Internet verbundenen Potenziale zu entfalten, ist es notwendig, dass sich Bürger*innen zur eigenen Suche motiviert und befähigt fühlen. Besonders entsprechende Fähigkeiten gilt es zu fördern, um das Risiko der Verstärkung informationaler, gesundheitlicher und sozialer Unterschiede zu reduzieren.
Keywords: Empowered patients; Health promotion; Health-realted online search; Uncertainty management.
References
-
- Galarce EM, Ramanadhan S, Viswanath K. Health information seeking. In: Thompson TL, Parrott R, Nussbaum JF, editors. The Routledge handbook of health communication. 2. New York: Routledge; 2011.
-
- Johnson JD, Case DO. Health information seeking. Bern: Peter Lang; 2012.
-
- Brashers DE, Neidig JL, Haas SM, Dobbs LK, Cardillo LW, Russell JA. Communication in the management of uncertainty. The case of persons living with HIV or AIDS. Commun Monogr. 2000;67(1):63–84. doi: 10.1080/03637750009376495. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources