Characterization and Cytotoxicity of Polyprenol Lipid and Vitamin E-TPGS Hybrid Nanoparticles for Betulinic Acid and Low-Substituted Hydroxyl Fullerenol in MHCC97H and L02 Cells
- PMID: 32368052
- PMCID: PMC7184125
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S249773
Characterization and Cytotoxicity of Polyprenol Lipid and Vitamin E-TPGS Hybrid Nanoparticles for Betulinic Acid and Low-Substituted Hydroxyl Fullerenol in MHCC97H and L02 Cells
Abstract
Background: This study demonstrated an innovative formulation including the polyprenol (GBP) lipid and vitamin E-TPGS hybrid nanoparticles (NPs) which was aimed to control the transfer of betulinic acid (BA) and low-substituted hydroxyl fullerenol (C60(OH)n). Additionally, it developed BA-C60(OH)n-GBP-TPGS-NPs delivery system and researched the anti-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) effects.
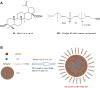
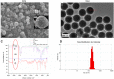
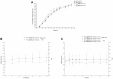
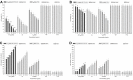
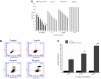
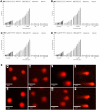
Materials and methods: The NPs were prepared by nanoprecipitation with ultrasonic-assisted emulsification (UAE) method. It was characterized by scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), FTIR spectrum, size distribution and zeta potential. Physical and chemical properties were evaluated through measurement of drug release, stability studies, drug loading efficiency (DE) and encapsulation efficiency (EE). Biological activities were evaluated through measurement of MTT assay, lactate dehydrogenase leakage assay (LDH), cell proliferation assays, cell apoptosis analysis, comet assay, wound healing assay, cell invasion and Western blot analysis.
Results and conclusions: The NPs exhibited clear distribution characteristics, improved solubility and stability. BA and C60(OH)n for the NPs displayed a biphasic release pattern with sustained drug release properties. The mixture of C60(OH)n with different hydroxyl groups may have a certain effect on the stability of the NPs system itself. The NPs could effectively inhibit MHCC97H cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. Combined use of C60(OH)n and BA in GBP lipids may improve the inhibit effect of C60(OH)n or BA against HCC cells and reduce cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of C60(OH)n for normal cells. We concluded that one of the important mechanisms of BA-C60(OH)n-GBP-TPGS-NPs inhibiting MHCC97H cells is achieved by up-regulating the expression of Caspase-3, Caspase-8 and Caspase-9.
Keywords: anti-tumor; betulinic acid; fullerenol; polyprenol; vitamin E-TPGS.
© 2020 Tao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

