PRMT5 Promotes Aerobic Glycolysis and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating the LXRα/NF-κBp65 Pathway
- PMID: 32368093
- PMCID: PMC7183334
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S239730
PRMT5 Promotes Aerobic Glycolysis and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating the LXRα/NF-κBp65 Pathway
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effects of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) on the biological function of breast cancer cells (BCCs) by regulating the liver X receptor α (LXRα)/NF-κBp65 pathway.
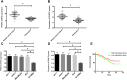
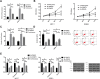
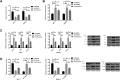
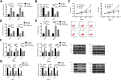
Methods: A total of 80 patients with breast cancer (BC) admitted to our hospital were collected, and 80 breast cancer tissue specimens and 80 corresponding tumor-adjacent tissue specimens were sampled from them for analysis. The reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was employed to determine the expression of PRMT5 mRNA in the sampled tissues, and the Western blot to determine the expression of LXRα and NF-κBp65 proteins in the tissues and cells. The patients were followed up to analyze their 3-year survival rate. Stable and transient overexpression vectors and inhibition vectors were constructed and transfected into BCCs. The cell counting kit-8 (CCK8), transwell, and flow cytometry were adopted to analyze the proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis of transfected cells, on which the effects of PRMT5 on LXRα and NF-κBp65 proteins were analyzed.
Results: PRMT5 was highly expressed in BC patients, and LXRα was lowly expressed in them, which had a high diagnostic value. Patients with high expression of PRMT5 showed a poor prognosis, and the expression of PRMT5 was related to the tumor size, pathological stage, differentiation, and metastatic in BC patients. Overexpressed PRMT5 enhanced the cell proliferation, invasion, and glycolysis abilities, weakened apoptosis ability, further lowered expression of LXRα and increased expression of NF-κBp65, while inhibited PRMT5 caused opposite results in those aspects. Up-regulating the expression of LXRα suppressed the proliferation, invasion, and aerobic glycolysis of BCCs and promoted their apoptosis, while inhibiting it posed opposite effects. The rescue experiment revealed that down-regulating the expression of PRMT5 could counteract the promotion of down-regulation of LXRα on proliferation, invasion and glycolysis of BCCs, and the nude mouse tumorigenesis test revealed that PRMT5 induced tumor on nude mice by mediating LXRα/NF-κBp65.
Conclusion: Inhibition of the PRMT5 expression can accelerate apoptosis of BCCs and weaken their proliferation, invasion, and aerobic glycolysis through the LXRα/NF-κBp65 pathway.
Keywords: LXRα; NF-κ BP65; PRMT5; biological function; breast cancer cell.
© 2020 Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PRMT5-activated c-Myc promote bladder cancer proliferation and invasion through up-regulating NF-κB pathway.Tissue Cell. 2022 Jun;76:101788. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2022.101788. Epub 2022 Mar 19. Tissue Cell. 2022. PMID: 35339800
-
Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Proliferation and Metastasis via LKB1/AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 May 28;9:645375. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.645375. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34124017 Free PMC article.
-
Liver X receptor α (LXRα) promoted invasion and EMT of gastric cancer cells by regulation of NF-κB activity.Hum Cell. 2017 Apr;30(2):124-132. doi: 10.1007/s13577-016-0157-3. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Hum Cell. 2017. PMID: 28091828
-
PRMT5 enhances tumorigenicity and glycolysis in pancreatic cancer via the FBW7/cMyc axis.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Mar 29;17(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0344-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 30922330 Free PMC article.
-
The methylation induced by protein arginine methyltransferase 5 promotes tumorigenesis and progression of lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Dec;10(12):7014-7019. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.10.100. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30746248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying Novel Cell Glycolysis-Related Gene Signature Predictive of Overall Survival in Gastric Cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Mar 12;2021:9656947. doi: 10.1155/2021/9656947. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33791386 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of PRMT5 in Cancers: A System Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancer Control. 2021 Jan-Dec;28:10732748211050583. doi: 10.1177/10732748211050583. Cancer Control. 2021. PMID: 34758643 Free PMC article.
-
Tadalafil increases the antitumor activity of 5-FU through inhibiting PRMT5-mediated glycolysis and cell proliferation in colorectal cancer.Cancer Metab. 2022 Dec 6;10(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40170-022-00299-4. Cancer Metab. 2022. PMID: 36474242 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Insights into Liver X Receptor α in the Tumorigenesis and Therapeutics of Human Cancers.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 28;13(8):1184. doi: 10.3390/biom13081184. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37627249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRMT5 promotes ovarian cancer growth through enhancing Warburg effect by methylating ENO1.MedComm (2020). 2023 Mar 28;4(2):e245. doi: 10.1002/mco2.245. eCollection 2023 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 36999124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thirumal Kumar D, Jain N, Evangeline J, et al. A computational approach for investigating the mutational landscape of RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1) and screening inhibitors against the oncogenic E17K mutation causing breast cancer. Comput Biol Med. 2019;115:103513. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103513 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

