Effects of miR-330-3p on Invasion, Migration and EMT of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting PRRX1-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 32368097
- PMCID: PMC7183782
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S238665
Effects of miR-330-3p on Invasion, Migration and EMT of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting PRRX1-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Retraction in
-
Effects of miR-330-3p on Invasion, Migration and EMT of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting PRRX1-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway [Retraction].Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Apr 5;17:299-300. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S472066. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38595927 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: miRNA, as a biological marker, had more and more attention in recent years due to the important role it plays in cancer. Currently, there are extensive studies on miRNAs, among which miR-330-3p is reported to be implicated in the pathophysiological processes of various cancers. However, little progress has been made in the mechanism of miR-330-3p in gastric cancer.
Objective: To explore the expression and relevant mechanism of miR-330-3p and PRRX1 in gastric cancer (GC).
Methods: Forty-five GC patients (study group), from whom paired GC and paracancerous tissues were collected, and another 45 healthy subjects (control group) who underwent physical examination during the same period were enrolled. In addition, GC cells and human gastric mucosa cells were purchased, and miR-330-3p-mimics, miR-330-3p-inhibitor, miR-NC, si-PRRX1, and sh-PRRX1 were transfected into MKN45, SGC7901 cell. QRT-PCR was employed to assess the miR-330-3p and PRRX1 expressions in the samples, and the cell expressions of PRRX1, GSK-3β, p-GSK-3β, β-catenin, p-β-catenin, cyclin D1, N-cadherin, E-cadherin and vimentin were evaluated by Western blot (WB). MTT, Transwell and wound-healing experiments were adopted to detect cell proliferation, invasion and migration.
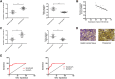
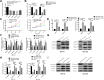
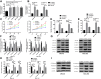
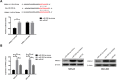
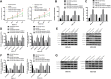
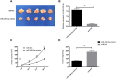
Results: MiR-330-3p was under-expressed, while PRRX1 was highly expressed in the serum of patients, both of which had an area under the curve (AUC) of more than 0.9. MiR-330-3p and PRRX1 were associated with tumor diameter, TNM staging, lymph node metastasis and differentiation of GC patients. Overexpression of miR-330-3p and inhibition of PRRX1 expression could suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of cells. What is more, WB assay showed that overexpressed miR-330-3p and inhibited PRRX1 could inhibit the expression levels of p-GSK-3β, β-catenin, cyclin D1, N-cadherin and vimentin proteins, while elevating GSK-3β, p-β-catenin and E-cadherin protein expressions. Dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed that there was a targeting relation between miR-330-3p and PRRX1. Furthermore, rescue experiments revealed that the cell proliferation, invasion, migration did not differ significantly between co-transfected miR-330-3p-mimics+sh-PRRX1, miR-330-3p-inhibitor+si-PRRX1 groups of MKN45 and SGC7901 and the miR-NC group (without transfected sequences).
Conclusion: Overexpressed miR-330-3p can promote cell EMT, proliferation, invasion and apoptosis through inhibiting PRRX1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which is expected to be a potential therapeutic target for GC.
Keywords: GC; PRRX1; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway; biological function; miR-330-3p.
© 2020 Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-19a-3p regulates the Forkhead box F2-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and affects the biological functions of colorectal cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Feb 14;26(6):627-644. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.627. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32103872 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of inhibition to Yes-related proteins-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through miR-195-5p on apoptosis of gastric cancer cells.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Aug;23(15):6486-6496. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201908_18532. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31378888
-
miR-143-3p inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating its target gene FGF1.Clin Transl Oncol. 2021 Mar;23(3):468-480. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02440-5. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32617870
-
Carboplatin Inhibits the Progression of Retinoblastoma Through IncRNA XIST/miR-200a-3p/NRP1 Axis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Aug 21;14:3417-3427. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S256813. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32904674 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling in gastric cancer: current progress and future prospects.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 7;14:1410513. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1410513. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38952556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive insight into the correlation between ncRNAs and the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in gastric cancer pathogenesis.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jun 29;21(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01092-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37386429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL1RN and PRRX1 as a Prognostic Biomarker Correlated with Immune Infiltrates in Colorectal Cancer: Evidence from Bioinformatic Analysis.Int J Genomics. 2022 Nov 29;2022:2723264. doi: 10.1155/2022/2723264. eCollection 2022. Int J Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36483329 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 Pathway in Gastric Cancer: Signaling, Therapeutic Targeting and Future Prospects.Biology (Basel). 2020 Jun 12;9(6):126. doi: 10.3390/biology9060126. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-149 Suppresses the Proliferation and Metastasis of Human Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting FOXC1.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Dec 17;2021:1503403. doi: 10.1155/2021/1503403. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34957298 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insight into Gastric Cancer Invasion-Current Status and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;16(1):54. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010054. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gan HH, Gunsalus KC. The role of tertiary structure in microRNA target recognition. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1970:43–64. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

