Protein phosphatase 1 activity controls a balance between collective and single cell modes of migration
- PMID: 32369438
- PMCID: PMC7200163
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.52979
Protein phosphatase 1 activity controls a balance between collective and single cell modes of migration
Abstract
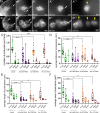
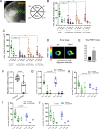
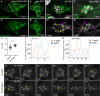
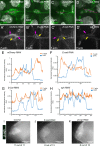
Collective cell migration is central to many developmental and pathological processes. However, the mechanisms that keep cell collectives together and coordinate movement of multiple cells are poorly understood. Using the Drosophila border cell migration model, we find that Protein phosphatase 1 (Pp1) activity controls collective cell cohesion and migration. Inhibition of Pp1 causes border cells to round up, dissociate, and move as single cells with altered motility. We present evidence that Pp1 promotes proper levels of cadherin-catenin complex proteins at cell-cell junctions within the cluster to keep border cells together. Pp1 further restricts actomyosin contractility to the cluster periphery rather than at individual internal border cell contacts. We show that the myosin phosphatase Pp1 complex, which inhibits non-muscle myosin-II (Myo-II) activity, coordinates border cell shape and cluster cohesion. Given the high conservation of Pp1 complexes, this study identifies Pp1 as a major regulator of collective versus single cell migration.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; cell adhesion; cell biology; cell collective; cell migration; developmental biology; myosin; protein phosphatases.
© 2020, Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
YC, NK, GA, LC, CM, AB, KS, DR, XW, JM No competing interests declared
Figures





References
-
- Ambach A, Saunus J, Konstandin M, Wesselborg S, Meuer SC, Samstag Y. The serine phosphatases PP1 and PP2A associate with and activate the actin-binding protein cofilin in human T lymphocytes. European Journal of Immunology. 2000;30:3422–3431. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(2000012)30:12<3422::AID-IMMU3422>3.0.CO;2-J. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

