Association of Blood Glucose Control and Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19 and Pre-existing Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 32369736
- PMCID: PMC7252168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021
Association of Blood Glucose Control and Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19 and Pre-existing Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
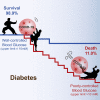
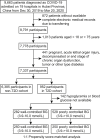
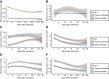
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a major comorbidity of COVID-19. However, the impact of blood glucose (BG) control on the degree of required medical interventions and on mortality in patients with COVID-19 and T2D remains uncertain. Thus, we performed a retrospective, multi-centered study of 7,337 cases of COVID-19 in Hubei Province, China, among which 952 had pre-existing T2D. We found that subjects with T2D required more medical interventions and had a significantly higher mortality (7.8% versus 2.7%; adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.49) and multiple organ injury than the non-diabetic individuals. Further, we found that well-controlled BG (glycemic variability within 3.9 to 10.0 mmol/L) was associated with markedly lower mortality compared to individuals with poorly controlled BG (upper limit of glycemic variability exceeding 10.0 mmol/L) (adjusted HR, 0.14) during hospitalization. These findings provide clinical evidence correlating improved glycemic control with better outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing T2D.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; blood glucose control; diabetes mellitus; mortality.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Type 2 diabetic Asian Indians and COVID-19: Lessons learnt so far from the ongoing pandemic.J Postgrad Med. 2020 Oct-Dec;66(4):179-181. doi: 10.4103/jpgm.JPGM_602_20. J Postgrad Med. 2020. PMID: 33037170 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Booth C.M., Matukas L.M., Tomlinson G.A., Rachlis A.R., Rose D.B., Dwosh H.A., Walmsley S.L., Mazzulli T., Avendano M., Derkach P. Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 144 patients with SARS in the greater Toronto area. JAMA. 2003;289:2801–2809. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein S.R., Rubino F., Khunti K., Mingrone G., Hopkins D., Birkenfeld A.L., Boehm B., Amiel S., Holt R.I., Skyler J.S. Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2. Published online April 23, 2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Candido R., Jandeleit-Dahm K.A., Cao Z., Nesteroff S.P., Burns W.C., Twigg S.M., Dilley R.J., Cooper M.E., Allen T.J. Prevention of accelerated atherosclerosis by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation. 2002;106:246–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

