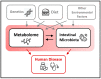
Metabolome-Microbiome Crosstalk and Human Disease
- PMID: 32369899
- PMCID: PMC7281736
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo10050181
Metabolome-Microbiome Crosstalk and Human Disease
Abstract
In this review, we discuss the growing literature demonstrating robust and pervasive associations between the microbiome and metabolome. We focus on the gut microbiome, which harbors the taxonomically most diverse and the largest collection of microorganisms in the human body. Methods for integrative analysis of these "omics" are under active investigation and we discuss the advances and challenges in the combined use of metabolomics and microbiome data. Findings from large consortia, including the Human Microbiome Project and Metagenomics of the Human Intestinal Tract (MetaHIT) and others demonstrate the impact of microbiome-metabolome interactions on human health. Mechanisms whereby the microbes residing in the human body interact with metabolites to impact disease risk are beginning to be elucidated, and discoveries in this area will likely be harnessed to develop preventive and treatment strategies for complex diseases.
Keywords: metabolomics; metagenomics; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
AAL has received author royalties from UpToDate, Inc. and consultant fees from AstraZeneca, LP. STW has received royalties from UpToDate, Inc. JL-S is a consultant to Metabolon Inc. KL-S and RSK have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R01HL141826/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125273/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL148178/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL123915/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155742/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141826/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL148178/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL123915/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL146980/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3OD023268/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES001247/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023268/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL146980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical