Oxidative Stress in DNA Repeat Expansion Disorders: A Focus on NRF2 Signaling Involvement
- PMID: 32369911
- PMCID: PMC7277112
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10050702
Oxidative Stress in DNA Repeat Expansion Disorders: A Focus on NRF2 Signaling Involvement
Abstract
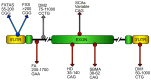
DNA repeat expansion disorders are a group of neuromuscular and neurodegenerative diseases that arise from the inheritance of long tracts of nucleotide repetitions, located in the regulatory region, introns, or inside the coding sequence of a gene. Although loss of protein expression and/or the gain of function of its transcribed mRNA or translated product represent the major pathogenic effect of these pathologies, mitochondrial dysfunction and imbalance in redox homeostasis are reported as common features in these disorders, deeply affecting their severity and progression. In this review, we examine the role that the redox imbalance plays in the pathological mechanisms of DNA expansion disorders and the recent advances on antioxidant treatments, particularly focusing on the expression and the activity of the transcription factor NRF2, the main cellular regulator of the antioxidant response.
Keywords: DNA repeat expansion disorders; FXTAS; Friedreich’s ataxia; Huntington’s disease; NRF2; fragile X syndrome; myotonic dystrophy; oxidative stress; spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy; spinocerebellar ataxia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

