Investigations of the Deuterium Permeability of As-Deposited and Oxidized Ti2AlN Coatings
- PMID: 32369946
- PMCID: PMC7254320
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13092085
Investigations of the Deuterium Permeability of As-Deposited and Oxidized Ti2AlN Coatings
Abstract
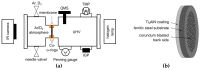
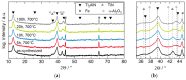
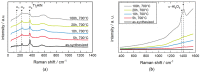
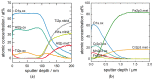
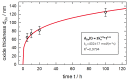
Aluminum containing Mn+1AXn (MAX) phase materials have attracted increasing attention due to their corrosion resistance, a pronounced self-healing effect and promising diffusion barrier properties for hydrogen. We synthesized Ti2AlN coatings on ferritic steel substrates by physical vapor deposition of alternating Ti- and AlN-layers followed by thermal annealing. The microstructure developed a {0001}-texture with platelet-like shaped grains. To investigate the oxidation behavior, the samples were exposed to a temperature of 700 °C in a muffle furnace. Raman spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) depth profiles revealed the formation of oxide scales, which consisted mainly of dense and stable α-Al2O3. The oxide layer thickness increased with a time dependency of ~t1/4. Electron probe micro analysis (EPMA) scans revealed a diffusion of Al from the coating into the substrate. Steel membranes with as-deposited Ti2AlN and partially oxidized Ti2AlN coatings were used for permeation tests. The permeation of deuterium from the gas phase was measured in an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) permeation cell by mass spectrometry at temperatures of 30-400 °C. We obtained a permeation reduction factor (PRF) of 45 for a pure Ti2AlN coating and a PRF of ~3700 for the oxidized sample. Thus, protective coatings, which prevent hydrogen-induced corrosion, can be achieved by the proper design of Ti2AlN coatings with suitable oxide scale thicknesses.
Keywords: MAX phase; PVD coating; Ti2AlN; hydrogen permeation; oxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Evans M.-H. An updated review: White etching cracks (WECs) and axial cracks in wind turbine gearbox bearings. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016;32:1133–1169. doi: 10.1080/02670836.2015.1133022. - DOI
-
- Farle A.-S., Kwakernaak C., van der Zwaag S., Sloof W.G. A conceptual study into the potential of Mn+1AXn-phase ceramics for self-healing of crack damage. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015;35:37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.08.046. - DOI
-
- Song G.M., Schnabel V., Kwakernaak C., van der Zwaag S., Schneider J.M., Sloof W.G. High temperature oxidation behaviour of Ti2AlC ceramic at 1200C. Mater. High Temp. 2012;29:205–209. doi: 10.3184/096034012X13348496462140. - DOI
-
- Hultman L. Thermal stability of nitride thin films. Vacuum. 2000;57:1–30. doi: 10.1016/S0042-207X(00)00143-3. - DOI
-
- Colonna F., Elsässer C. First principles DFT study of interstitial hydrogen and oxygen atoms in the MAX phase Ti2AlN. RSC Adv. 2017;7:37852–37857. doi: 10.1039/C7RA05045C. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

