Investigating an Integrated Sensor Fusion System for Mental Fatigue Assessment for Demanding Maritime Operations
- PMID: 32370110
- PMCID: PMC7248988
- DOI: 10.3390/s20092588
Investigating an Integrated Sensor Fusion System for Mental Fatigue Assessment for Demanding Maritime Operations
Abstract
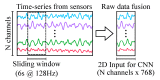
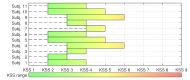
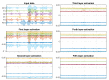
Human-related issues are currently the most significant factor in maritime causalities, especially in demanding operations that require coordination between two or more vessels and/or other maritime structures. Some of these human-related issues include incorrect, incomplete, or nonexistent following of procedures; lack of situational awareness; and physical or mental fatigue. Among these, mental fatigue is especially dangerous, due to its capacity to reduce reaction time, interfere in the decision-making process, and affect situational awareness. Mental fatigue is also especially hard to identify and quantify. Self-assessment of mental fatigue may not be reliable and few studies have assessed mental fatigue in maritime operations, especially in real time. In this work we propose an integrated sensor fusion system for mental fatigue assessment using physiological sensors and convolutional neural networks. We show, by using a simulated navigation experiment, how data from different sensors can be fused into a robust mental fatigue assessment tool, capable of achieving up to 100 % detection accuracy for single-subject classification. Additionally, the use of different sensors seems to favor the representation of the transition between mental fatigue states.
Keywords: deep learning; maritime operations; mental fatigue; physiological sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures










References
-
- Chauvin C. Human factors and maritime safety. J. Navig. 2011;64:625–632. doi: 10.1017/S0373463311000142. - DOI
-
- Schröder-Hinrichs J.U., Hollnagel E., Baldauf M., Hofmann S., Kataria A. Maritime human factors and IMO policy. Marit. Policy Manag. 2013;40:243–260. doi: 10.1080/03088839.2013.782974. - DOI
-
- Endsley M.R. Situation awareness global assessment technique (SAGAT); Proceedings of the IEEE 1988 National Aerospace and Electronics Conference; Dayton, OH, USA. 23–27 May 1988; pp. 789–795.
-
- Sneddon A., Mearns K., Flin R. Stress, fatigue, situation awareness and safety in offshore drilling crews. Saf. Sci. 2013;56:80–88. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2012.05.027. - DOI
-
- Quick J.C., Wright T.A., Adkins J.A., Nelson D.L., Quick J.D. Preventive Stress Management in Organizations. American Psychological Association; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

