Outcome Expectations for Exercise and Decisional Balance Questionnaires Predict Adherence and Efficacy of Exercise Programs in Dialysis Patients
- PMID: 32370202
- PMCID: PMC7246788
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17093175
Outcome Expectations for Exercise and Decisional Balance Questionnaires Predict Adherence and Efficacy of Exercise Programs in Dialysis Patients
Abstract
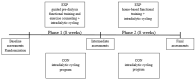
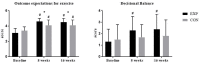
The purpose of this study was to define if Outcomes Expectations for Exercise (OEE) and Decisional Balance (DB) scales predict adherence to guided exercise programs and associate with the improvement in physical performance in the dialysis population. Participants (n = 40; age 63.6 ± 12.5 years) completed OEE and DB questionnaires before randomization to the experimental group (n = 20) and control group (n = 20) of a two-phased exercise program-the experimental group received eight weeks of supervised functional exercise and exercise counseling (1st phase) before commencing eight weeks of home-based exercise on non-dialysis days (2nd phase). Both groups performed intradialytic cycling on dialysis days during both study phases. Patients with above-median OEE and DB scores (>3.15 and >1.3, respectively) expressed significantly better adherence to intradialytic cycling (89% vs. 76%, 89% vs. 77%, respectively, p < 0.05). Experimental group patients with an above-median OEE (but not DB) score had significantly better adherence to supervised and home-based functional exercise (93% vs. 81% and 85% vs. 60%, respectively, p < 0.05). Baseline DB score predicted the final result in the hand-grip test and 6-min walk test. Low OEE and, to a lesser degree, low DB questionnaire scores associate with inferior adherence to dialysis bundled and home-based exercise programs and may help define patient subsets in need of intensified motivational input by exercise caregivers.
Keywords: adherence; behavior change; decisional balance; exercise adoption; functional training; hemodialysis; intradialytic cycling; outcomes expectations for exercise; questionnaire.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shlipak M.G., Fried L.F., Cushman M., Manolio T.A., Peterson D., Stehman-Breen C., Bleyer A., Newman A., Siscovick D., Psaty B. Cardiovascular mortality risk in chronic kidney disease: Comparison of traditional and novel risk factors. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005;293:1737–1745. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.14.1737. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

