SARS-CoV-2 was already spreading in France in late December 2019
- PMID: 32371096
- PMCID: PMC7196402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106006
SARS-CoV-2 was already spreading in France in late December 2019
Abstract
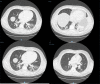
The COVID-19 epidemic is believed to have started in late January 2020 in France. Here we report a case of a patient hospitalised in December 2019 in an intensive care unit in a hospital in the north of Paris for haemoptysis with no aetiological diagnosis. RT-PCR was performed retrospectively on the stored respiratory sample and confirmed the diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Based on this result, it appears that the COVID-19 epidemic started much earlier in France.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus disease 2019; France; Intensive care unit; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. and International Society of Chemotherapy. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020.https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-8-opening-re...[accessed 30 April 2020].
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

