Loss of HAT1 expression confers BRAFV600E inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells by activating MAPK signaling via IGF1R
- PMID: 32371878
- PMCID: PMC7200761
- DOI: 10.1038/s41389-020-0228-x
Loss of HAT1 expression confers BRAFV600E inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells by activating MAPK signaling via IGF1R
Abstract
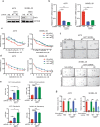
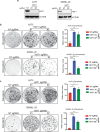
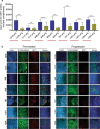
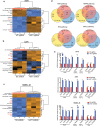
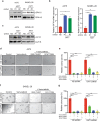
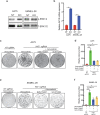
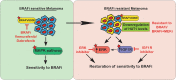
BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) have been approved for the clinical treatment of BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma. Although initial responses to BRAFi are generally favorable, acquired BRAFi resistance emerges rapidly, resulting in treatment failure. Only some of the underlying mechanisms responsible for BRAFi resistance are currently understood. Here, we showed that the genetic inhibition of histone acetyltransferase 1 (HAT1) in BRAF-mutant melanoma cells resulted in BRAFi resistance. Using quantitative immunofluorescence analysis of patient sample pairs, consisting of pre-treatment along with matched progressed BRAFi + MEKi-treated melanoma samples, HAT1 downregulation was observed in 7/11 progressed samples (~63%) in comparison with pre-treated samples. Employing NanoString-based nCounter PanCancer Pathway Panel-based gene expression analysis, we identified increased MAPK, Ras, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and Wnt pathway activation in HAT1 expression inhibited cells. We further found that MAPK pathway activation following the loss of HAT1 expression was partially driven by increased insulin growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) signaling. We showed that both MAPK and IGF1R pathway inhibition, using the ERK inhibitor SCH772984 and the IGF1R inhibitor BMS-754807, respectively, restored BRAFi sensitivity in melanoma cells lacking HAT1. Collectively, we show that the loss of HAT1 expression confers acquired BRAFi resistance by activating the MAPK signaling pathway via IGF1R.
Conflict of interest statement
D.B.J. serves on advisory boards for Array Biopharma, BMS, Jansen, Merck, and Novartis, and receives research funding from BMS and Incyte. E.S.Y. serves on advisory boards for Strata Oncology, AstraZeneca and Bayer, serves as consultant for Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca, and receives research funding from Eli Lilly, Novartis, and PUMA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of BOP1 confers resistance to BRAF kinase inhibitors in melanoma by activating MAP kinase pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 5;116(10):4583-4591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821889116. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30782837 Free PMC article.
-
ER Translocation of the MAPK Pathway Drives Therapy Resistance in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma.Cancer Discov. 2019 Mar;9(3):396-415. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0348. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 30563872 Free PMC article.
-
Activity and Resistance of a Brain-Permeable Paradox Breaker BRAF Inhibitor in Melanoma Brain Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2022 Jul 18;82(14):2552-2564. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-4152. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35584009
-
Immunomodulatory effects of BRAF and MEK inhibitors: Implications for Melanoma therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Oct;136:151-159. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30145328 Review.
-
Targeted Therapy in Melanoma and Mechanisms of Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 27;21(13):4576. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134576. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32605090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Phase II Exploratory Study to Identify Biomarkers Predictive of Clinical Response to Regorafenib in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Who Have Failed First-Line Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 19;25(1):43. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010043. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203214 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Conquering oncogenic KRAS and its bypass mechanisms.Theranostics. 2022 Jul 18;12(13):5691-5709. doi: 10.7150/thno.71260. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35966590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in the Transcriptome and Chromatin Landscape in BRAFi-Resistant Melanoma Cells.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 17;12:937831. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.937831. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35785205 Free PMC article.
-
Disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like promotes ovarian cancer tumor growth by stimulating pro-tumorigenic metabolic pathways and blocking apoptosis.Oncogenesis. 2021 Jul 12;10(7):48. doi: 10.1038/s41389-021-00339-6. Oncogenesis. 2021. PMID: 34253709 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ signaling sensitizes MEKi-resistant human melanoma to targeted therapy-induced apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Dec 21;15(12):925. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07305-1. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39709491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aladowicz E, et al. Molecular networks in melanoma invasion and metastasis. Future Oncol. 2013;9:713–726. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- R01CA200919/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 CA200919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA221926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA090625/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03CA230815/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R03 CA230815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA196566/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R21 CA229927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21CA229927/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 CA196566/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

