Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks
- PMID: 32371934
- PMCID: PMC8238571
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-020-0843-2
Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks.Nat Med. 2020 Jun;26(6):981. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0946-9. Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 32461699 Free PMC article.
Abstract
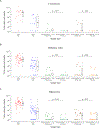
We identified seasonal human coronaviruses, influenza viruses and rhinoviruses in exhaled breath and coughs of children and adults with acute respiratory illness. Surgical face masks significantly reduced detection of influenza virus RNA in respiratory droplets and coronavirus RNA in aerosols, with a trend toward reduced detection of coronavirus RNA in respiratory droplets. Our results indicate that surgical face masks could prevent transmission of human coronaviruses and influenza viruses from symptomatic individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
BJC consults for Roche and Sanofi Pasteur. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Respiratory protection for healthcare workers caring for COVID-19 patients.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2020 Sep;41(9):1064-1065. doi: 10.1017/ice.2020.175. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 32321614 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

