PD-L1 and HER2 Expression in Gastroesophageal Cancer: a Matched Case Control Study
- PMID: 32372174
- PMCID: PMC7471145
- DOI: 10.1007/s12253-020-00814-2
PD-L1 and HER2 Expression in Gastroesophageal Cancer: a Matched Case Control Study
Abstract
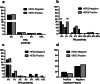
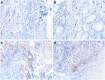
Immunotherapy with check-point inhibitors serves as a promising treatment strategy in patients with upper gastrointestinal (GI) tumors. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is the only identified therapeutic target in upper GI tumors, whose potential interaction with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is unknown. The aim of this study was the investigation of PD-L1 and HER2 in upper GI tumors. We retrospectively identified patients with HER2 positive gastroesophageal cancers and matched them with a HER2 negative group. We investigated the tumor specimens for HER2 status and PD-L1 expression, with the following assessments being performed: i) staining of tumor cells in terms of tumor proportion score (TPS), ii) staining for tumor-associated immune cells (TAIs), iii) interface pattern and iv) combined positive score (CPS). Both HER2 positive and negative group consisted of 59 patients. Expression of PD-L1 in TAIs and interface pattern were associated with a favorable outcome (p = 0.02, HR = 0.8; p = 0.04, HR = 0.39; respectively) in patients with localized disease, whereas TPS was associated with an unfavorable outcome in patients with advanced tumor (p = 0.02, HR = 1.4). These effects were HER2 independent. PD-L1 expression in its different assessment is equally observed in HER2 positive and negative patients. Future studies will show whether dual inhibition of HER2 and PD-L1 improves survival of this selected patient population.
Keywords: CPS; Esophageal tumor; Gastric tumor; Gastroesophageal junction tumor; Gastroesophageal tumor; HER2; Immunotherapy; PD-L1; TPS.
Conflict of interest statement
HC.P. has received travel support from Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche.
M.P. has received honoraria for lectures, consultation or advisory board participation from the following for-profit companies: Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Gerson Lehrman Group (GLG), CMC Contrast, GlaxoSmithKline, Mundipharma, Roche, MedMedia, Astra Zeneca, AbbVie, Lilly, Medahead, Daiichi Sankyo, Merck Sharp & Dome.
A.I-M. participated in advisory boards from MSD and Servier, received lecture honoraria from Eli Lilly and Servier, is the local PI for clinical trials sponsored by BMS and Astellas.
Other authors have nothing to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Cho J, Lee J, Bang H, Kim ST, Park SH, An JY, Choi MG, Lee JH, Sohn TS, Bae JM, Kang WK, Kim S, Kim KM (2017) Programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression predicts survival in patients with gastric carcinoma with microsatellite instability. Oncotarget 8 (8):13320-13328. 10.18632/oncotarget.14519 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD, Sosman JA, Atkins MB, Leming PD, Spigel DR, Antonia SJ, Horn L, Drake CG, Pardoll DM, Chen L, Sharfman WH, Anders RA, Taube JM, McMiller TL, Xu H, Korman AJ, Jure-Kunkel M, Agrawal S, McDonald D, Kollia GD, Gupta A, Wigginton JM, Sznol M. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2443–2454. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

