Cyclic AMP in dendritic cells: A novel potential target for disease-modifying agents in asthma and other allergic disorders
- PMID: 32372523
- PMCID: PMC7348084
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.15095
Cyclic AMP in dendritic cells: A novel potential target for disease-modifying agents in asthma and other allergic disorders
Abstract
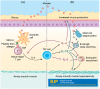
Allergic diseases are immune disorders that are a global health problem, affecting a large portion of the world's population. Allergic asthma is a heterogeneous disease that alters the biology of the airway. A substantial portion of patients with asthma do not respond to conventional therapies; thus, new and effective therapeutics are needed. Dendritic cells (DCs), antigen presenting cells that regulate helper T cell differentiation, are key drivers of allergic inflammation but are not the target of current therapies. Here we review the role of dendritic cells in allergic conditions and propose a disease-modifying strategy for treating allergic asthma: cAMP-mediated inhibition of dendritic cells to blunt allergic inflammation. This approach contrasts with current treatments that focus on treating clinical manifestations of airway inflammation. Disease-modifying agents that target cAMP and its signalling pathway in dendritic cells may provide a novel means to treat asthma and other allergic diseases.
© 2020 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aandahl, E. M. , Moretto, W. J. , Haslett, P. A. , Vang, T. , Bryn, T. , Tasken, K. , & Nixon, D. F. (2002). Inhibition of antigen‐specific T cell proliferation and cytokine production by protein kinase A type I. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 169(2), 802–808. 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.802 - DOI - PubMed

