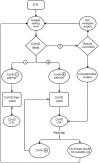
Orthopaedic patient workflow in CoViD-19 pandemic in Italy
- PMID: 32372852
- PMCID: PMC7195001
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2020.04.006
Orthopaedic patient workflow in CoViD-19 pandemic in Italy
Abstract
CoViD-19 epidemic started in China in late December 2019, and soon spread, turning into a pandemic. All medical specialties have soon been involved in the management of CoViD-19 patients; the daily Orthopaedic activity has been affected profoundly by this dramatic health emergency. The present paper aims to summarize all the measures and changes that had to be made in order to avoid the healthcare system collapse in the most affected areas, and provides an operative flowchart.
Keywords: Covid; Management; Pandemia.
© 2020 Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors had nothing to disclose about conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, et al; China medical treatment expert group for CoViD-19. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032.
-
- coronavirus disease 2019 (CoViD-19) https://www.who.intSituation report - 72
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources