Ginsenosides: potential therapeutic source for fibrosis-associated human diseases
- PMID: 32372860
- PMCID: PMC7195584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.12.003
Ginsenosides: potential therapeutic source for fibrosis-associated human diseases
Abstract
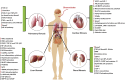
Tissue fibrosis is an eventual pathologic change of numerous chronic illnesses, which is characterized by resident fibroblasts differentiation into myofibroblasts during inflammation, coupled with excessive extracellular matrix deposition in tissues, ultimately leading to failure of normal organ function. Now, there are many mechanistic insights into the pathogenesis of tissue fibrosis, which facilitate the discovery of effective antifibrotic drugs. Moreover, many chronic diseases remain a significant clinical unmet need. For the past five years, many research works have undoubtedly addressed the functional dependency of ginsenosides in different types of fibrosis and the successful remission in various animal models treated with ginsenosides. Caveolin-1, interleukin, thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), liver X receptors (LXRs), Nrf2, microRNA-27b, PPARδ-STAT3, liver kinase B1 (LKB1)-AMPK, and TGF-β1/Smads are potential therapy targeting using ginsenosides. Ginsenosides can play a targeting role and suppress chronic inflammatory response, collagen deposition, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), as well as myofibroblast activation to attenuate fibrosis. In this report, our aim was to focus on the therapeutic prospects of ginsenosides in fibrosis-related human diseases making use of results acquired from various animal models. These findings should provide important therapeutic clues and strategies for the exploration of new drugs for fibrosis treatment.
Keywords: Chinese herb medicines; Fibrosis; Ginseng; Ginsenosides; Therapeutics.
© 2020 The Korean Society of Ginseng, Published by Elsevier Korea LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Featured Article: TGF-β1 dominates extracellular matrix rigidity for inducing differentiation of human cardiac fibroblasts to myofibroblasts.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Apr;243(7):601-612. doi: 10.1177/1535370218761628. Epub 2018 Mar 4. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 29504479 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor β1 signaling coincides with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in the development of adenomyosis in mice.Hum Reprod. 2016 Feb;31(2):355-69. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev314. Epub 2015 Dec 20. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 26689216
-
Corroborating evidence for platelet-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in the development of adenomyosis.Hum Reprod. 2016 Apr;31(4):734-49. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew018. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 26908845
-
The origin of renal fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and the signals that trigger fibrosis.Differentiation. 2016 Sep;92(3):102-107. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Differentiation. 2016. PMID: 27262400 Review.
-
Natural Products as a Source for Antifibrosis Therapy.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Nov;39(11):937-952. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30268571 Review.
Cited by
-
The potential therapeutic role of melatonin in organ fibrosis: a comprehensive review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 13;11:1502368. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1502368. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39735699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discrepancy Study of the Chemical Constituents of Panax Ginseng from Different Growth Environments with UPLC-MS-Based Metabolomics Strategy.Molecules. 2023 Mar 24;28(7):2928. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072928. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049688 Free PMC article.
-
Ginseng saponin metabolite 20(S)-protopanaxadiol relieves pulmonary fibrosis by multiple-targets signaling pathways.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Jul;47(4):543-551. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.01.002. Epub 2023 Jan 7. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 37397411 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of Korean red ginseng water extract on levothyroxine-induced hyperthyroidism and propylthiouracil-induced hypothyroidism in rats.Integr Med Res. 2024 Sep;13(3):101071. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2024.101071. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Integr Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39263445 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cGAS-STING signaling in pulmonary fibrosis and its therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 25;14:1273248. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273248. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37965345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rockey D.C., Bell P.D., Hill J.A. Fibrosis--a common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1138–1149. - PubMed
-
- Gurtner G.C., Werner S., Barrandon Y., Longaker M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453:314–321. - PubMed
-
- Stramer B.M., Mori R., Martin P. The inflammation-fibrosis link? A Jekyll and Hyde role for blood cells during wound repair. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127:1009–1017. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

