Comparative transcriptome analysis of the protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against the influence of bisphenol A in the liver and uterus of ovariectomized mice
- PMID: 32372874
- PMCID: PMC7195581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.01.008
Comparative transcriptome analysis of the protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against the influence of bisphenol A in the liver and uterus of ovariectomized mice
Abstract
Background: Bisphenol A (BPA), known as an endocrine disruptor, is widely used in the world. BPA is reported to cause inflammation-related diseases. Korean Red Ginseng (KRG) has been used safely in human for a long time for the treatment of diverse diseases. KRG has been reported of its mitigating effect on menopausal symptoms and suppress adipose inflammation. Here, we investigate the protective effect of orally administered KRG on the impacts of BPA in the liver and uterus of menopausal mice model.
Methods: The transcriptome analysis for the effects of BPA on mice liver was evaluated by Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database-based data (GSE26728). In vivo assay to evaluate the protective effect of KRG on BPA impact in ovariectomized (OVX) mice were designed and analyzed by RNA sequencing.
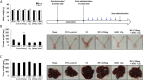
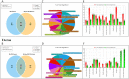
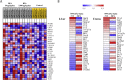
Results: We first demonstrated that BPA induced 12 kinds of gene set in the liver of normal mice. The administration of BPA and KRG did not change body, liver, and uterine weight in OVX mice. KRG downregulated BPA-induced inflammatory response and chemotaxis-related gene expression. Several gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)-derived inflammatory response genes increased by BPA were inhibited by KRG in OVX mice.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that BPA has commonly influenced inflammatory response effects on both normal and OVX mice. KRG protects against BPA impact of inflammatory response and chemotaxis in OVX mouse models. Our comparative analysis will provide new insight into the efficacy of KRG on endocrine disrupting chemicals and OVX mouse.
Keywords: Bisphenol A; Korean Red Ginseng; Transcriptome analysis.
© 2020 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on Bisphenol A-Induced Fatty Acid Composition and Lipid Metabolism-Related Gene Expression Changes.Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(8):1841-1858. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X20500925. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Am J Chin Med. 2020. PMID: 33300480
-
Effects of Korean red ginseng (Panax Ginseng Meyer) on bisphenol A exposure and gynecologic complaints: single blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jul 25;14:265. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-265. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25063041 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Korean Red Ginseng suppresses bisphenol A-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and cellular migration of A549 human lung cancer cell through inhibition of reactive oxygen species.J Ginseng Res. 2021 Jan;45(1):119-125. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.01.002. Epub 2020 Jan 14. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 33437163 Free PMC article.
-
Ginseng, the natural effectual antiviral: Protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against viral infection.J Ginseng Res. 2016 Oct;40(4):309-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Ginseng Res. 2016. PMID: 27746682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on metabolic syndrome.J Ginseng Res. 2021 May;45(3):380-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34025131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KRG and its major ginsenosides do not show distinct steroidogenic activities examined by the OECD test guideline 440 and 456 assays.J Ginseng Res. 2023 May;47(3):385-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.09.002. Epub 2022 Oct 5. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 37252278 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of medicinal plants and their beneficial roles in alleviating bisphenol A-induced organ toxicity.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):7801-7876. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03795-8. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39932506 Review.
-
Korean Red Ginseng exerts anti-inflammatory and autophagy-promoting activities in aged mice.J Ginseng Res. 2021 Nov;45(6):717-725. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.03.009. Epub 2021 Apr 6. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34764726 Free PMC article.
-
The beneficial potential of ginseng for menopause.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Sep;48(5):449-453. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.05.008. Epub 2024 May 31. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 39263310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of red ginseng on gut, microbiota, and brain in a mouse model of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome.J Ginseng Res. 2021 Nov;45(6):706-716. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.03.008. Epub 2021 Apr 3. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34764725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murata M., Kang J.H. Bisphenol A (BPA) and cell signaling pathways. Biotechnology Advances. 2018;36(1):311–327. - PubMed
-
- Vermeirssen E.L., Dietschweiler C., Werner I., Burkhardt M. Corrosion protection products as a source of bisphenol A and toxicity to the aquatic environment. Water Research. 2017;123:586–593. - PubMed
-
- Vitku J., Kolatorova L., Franekova L., Blahos J., Simkova M., Duskova M., Skodova T., Starka L. Endocrine disruptors of the bisphenol and paraben families and bone metabolism. Physiological Research. 2018;67 - PubMed
-
- Skledar D.G., Mašič L.P. Bisphenol A and its analogs: do their metabolites have endocrine activity? Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2016;47:182–199. - PubMed
-
- Park C., Lee J., Kong B., Park J., Song H., Choi K., Guon T., Lee Y. The effects of bisphenol A, benzyl butyl phthalate, and di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on estrogen receptor alpha in estrogen receptor-positive cells under hypoxia. Environmental Pollution. 2019;248:774–781. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

