Interplay between inflammation and cancer
- PMID: 32372882
- PMCID: PMC7191124
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2020.04.004
Interplay between inflammation and cancer
Abstract
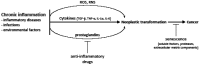
Tumor-promoting inflammation is one of the hallmarks of cancer. It has been shown that cancer development is strongly influenced by both chronic and acute inflammation process. Progress in research on inflammation revealed a connection between inflammatory processes and neoplastic transformation, the progression of tumour, and the development of metastases and recurrences. Moreover, the tumour invasive procedures (both surgery and biopsy) affect the remaining tumour cells by increasing their survival, proliferation and migration. One of the concepts explaining this phenomena is an induction of a wound healing response. While in normal tissue it is necessary for tissue repair, in tumour tissue, induction of adaptive and innate immune response related to wound healing, stimulates tumour cell survival, angiogenesis and extravasation of circulating tumour cells. It has become evident that certain types of immune response and immune cells can promote tumour progression more than others. In this review, we focus on current knowledge on carcinogenesis and promotion of cancer growth induced by inflammatory processes.
Keywords: ANGPTL4, angiopoietin-like 4; CDH1, cadherin 1; COX, cyclooxygenase; Cancer; EMT, epithelail to mesenchymal transition; EP, receptor - prostaglandin receptor; GI, gastrointensinal cancer; IL-6, interleukin 6; Inflammation; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NADPH, nicotynamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NK, natural killer cells; NO, nitric oxide; NSAIDs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; PTHrP, parathyroid hormone related protein; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxigen species; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TGFBRII, transforming growth factor, beta receptor II; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor α; TNFR1, Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1; TNFR2, Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2; Tumor reccurence; VEGF, vascular endothelail growth factor; bFGF, fibroblast growth factor; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- J., M., in Dictionnaire de medicine. 1828: Paris. p. 31-50.
-
- C., H., On warty tumors in cicatrices. Lond Med Gaz, 1833(13): p. 481-2.
-
- Schmidt A., Weber O.F. In memoriam of Rudolf virchow: A historical retrospective including aspects of inflammation, infection and neoplasia. Contrib Microbiol. 2006;13:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Pisani P. Cancer and infection: Estimates of the attributable fraction in 1990. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1997;6(6):387–400. - PubMed
-
- Shacter E., Weitzman S.A. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park, NY) 2002;16(2):217–226. 229; discussion 230-2. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous