Improved Resting-State Functional Dynamics in Post-stroke Depressive Patients After Shugan Jieyu Capsule Treatment
- PMID: 32372901
- PMCID: PMC7177051
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00297
Improved Resting-State Functional Dynamics in Post-stroke Depressive Patients After Shugan Jieyu Capsule Treatment
Abstract
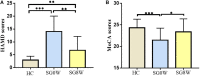
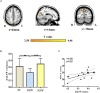
Shugan Jieyu Capsule (SG), a Chinese herbal medicine mainly composed of Acanthopanax and Hypericum perforatum, has been used to ameliorate cognitive impairments and emotional problems induced by post-stroke depression (PSD), while the altered brain dynamics underlying the ameliorative effects of SG have remained unclear. Our study focused on investigating the potential neurobiological mechanisms of SG in improving the cognitive function of PSD patients via resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Fifteen PSD patients (mean ages: 64.13 ± 6.01 years) were instructed to take 0.72 g of SG twice a day for 8 weeks. PSD patients underwent fMRIs, the 24-item Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD-24) and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) at baseline and the end of intervention, and these assessments were also performed on twenty-one healthy controls (HC) (mean ages: 60.67 ± 6.95 years). Additionally, the dynamic amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (dALFF) and functional connectivity (dFC) were determined to reveal changes in dynamic functional patterns. We found that taking SG significantly reduced the depressive symptoms assessed by HAMD-24 and improved cognitive functions assessed by MoCA in PSD patients. Furthermore, at baseline, PSD patients showed decreased dALFF in the right precuneus and increased dFC between the right precuneus and left angular gyrus, compared with HC. After intervention, the dALFF and dFC variances of the abnormal patterns were reversed. Additionally, the dALFF variance in the right precuneus was positively correlated with MoCA scores in PSD patients after SG treatment. Collectively, our results indicate that SG may improve the cognitive function of PSD patients through alteration of brain dynamics. Our findings lay a foundation for the exploration of the neurobiological mechanisms of SG in ameliorating symptoms of PSD patients.
Keywords: Shugan Jieyu Capsule; cognitive function; dynamic amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations; dynamic functional connectivity; functional magnetic resonance imaging; post-stroke depression.
Copyright © 2020 Yao, Li, Wang, Liu, Li, Cao, Chen and Xu.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

