Angelicin-A Furocoumarin Compound With Vast Biological Potential
- PMID: 32372949
- PMCID: PMC7176996
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00366
Angelicin-A Furocoumarin Compound With Vast Biological Potential
Abstract
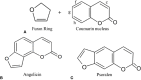
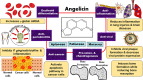
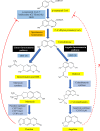
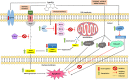
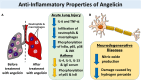
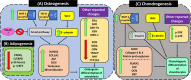
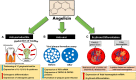
Angelicin, a member of the furocoumarin group, is related to psoralen which is well known for its effectiveness in phototherapy. The furocoumarins as a group have been studied since the 1950s but only recently has angelicin begun to come into its own as the subject of several biological studies. Angelicin has demonstrated anti-cancer properties against multiple cell lines, exerting effects via both the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways, and also demonstrated an ability to inhibit tubulin polymerization to a higher degree than psoralen. Besides that, angelicin too demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity in inflammatory-related respiratory and neurodegenerative ailments via the activation of NF-κB pathway. Angelicin also showed pro-osteogenesis and pro-chondrogenic effects on osteoblasts and pre-chondrocytes respectively. The elevated expression of pro-osteogenic and chondrogenic markers and activation of TGF-β/BMP, Wnt/β-catenin pathway confirms the positive effect of angelicin bone remodeling. Angelicin also increased the expression of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) in osteogenesis. Other bioactivities, such as anti-viral and erythroid differentiating properties of angelicin, were also reported by several researchers with the latter even displaying an even greater aptitude as compared to the commonly prescribed drug, hydroxyurea, which is currently on the market. Apart from that, recently, a new application for angelicin against periodontitis had been studied, where reduction of bone loss was indirectly caused by its anti-microbial properties. All in all, angelicin appears to be a promising compound for further studies especially on its mechanism and application in therapies for a multitude of common and debilitating ailments such as sickle cell anaemia, osteoporosis, cancer, and neurodegeneration. Future research on the drug delivery of angelicin in cancer, inflammation and erythroid differentiation models would aid in improving the bioproperties of angelicin and efficacy of delivery to the targeted site. More in-depth studies of angelicin on bone remodeling, the pro-osteogenic effect of angelicin in various bone disease models and the anti-viral implications of angelicin in periodontitis should be researched. Finally, studies on the binding of angelicin toward regulatory genes, transcription factors, and receptors can be done through experimental research supplemented with molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation.
Keywords: angelicin; biological activities; biological potential; furocoumarin; psolaren.
Copyright © 2020 Mahendra, Tan, Lee, Yap, Pusparajah, Low, Tang, Chan, Lee and Goh.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

