Xiaochaihutang Improves the Cortical Astrocyte Edema in Thioacetamide-Induced Rat Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy by Activating NRF2 Pathway
- PMID: 32372950
- PMCID: PMC7179068
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00382
Xiaochaihutang Improves the Cortical Astrocyte Edema in Thioacetamide-Induced Rat Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy by Activating NRF2 Pathway
Abstract
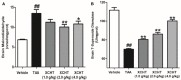
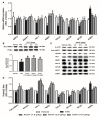
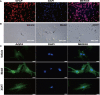
Oxidative stress induced by high ammonia, which leads to astrocyte edema, is the key to acute hepatic encephalopathy (AHE). Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) has been implicated in oxidative stress, but the mechanism of NRF2 against ammonia-induced astrocytes edema has not been fully studied. We confirmed that the NRF2 pathway is related to brain edema caused by AHE and found that Xiaochaihutang (XCHT) could effectively activate the NRF2 pathway to treat AHE. The model of AHE was established with thioacetamide (TAA) in rats. Rat behaviors were observed, brain water content, blood ammonia levels, glutamine synthetase (GS), malondialdehyde (MDA), and total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) were determined after XCHT treatment. Furthermore, the expression of NRF2 pathway proteins and mRNA, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and aquaporins 4 (AQP4) were examined. In order to determine whether XCHT has a direct effect on cerebral edema caused by high ammonia, we examined the effect of XCHT compound serum on cortical astrocytes in the presence of ammonia, through microscopic observation and immunofluorescence (IF). Results showed that AHE induced by TAA changed the behavior of the rats, and increased brain water content, blood ammonia levels, GS and MDA content meanwhile decreasing T-SOD, but these symptoms were improved by treatment with XCHT. XCHT protected brain edema by activating the NRF2 pathway and increasing the expression of downstream proteins and genes. Astrocytes treated with 5 mM ammonia also showed an increase in the AQP4 protein expression but a decrease in XCHT compound serum and ammonia-induced cell edema groups. This study demonstrates that the NRF2 pathway is involved in the brain edema in AHE, and XCHT may represent a useful prescription for the treatment of AHE.
Keywords: NRF2 pathway; Xiaochaihutang; acute hepatic encephalopathy; astrocyte edema; brain edema.
Copyright © 2020 Jia, Liu, Hu, Hu, Tang, Li and Li.
Figures



References
-
- Cao L.-J., Li H.-D., Yan M., Li Z.-H., Gong H., Jiang P., et al. (2016). The protective effects of isoliquiritigenin and glycyrrhetinic acid against triptolide-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells involve Nrf2 activation. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 8912184. 10.1155/2016/8912184 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

