Short-Term Central Adaptation in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- PMID: 32373046
- PMCID: PMC7186433
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00260
Short-Term Central Adaptation in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Abstract
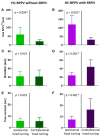
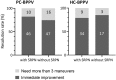
Objective: To elucidate the frequency, underlying mechanisms, and clinical implications of spontaneous reversal of positional nystagmus (SRPN) in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Methods: We prospectively recruited 182 patients with posterior canal (PC, n = 119) and horizontal canal (HC) BPPV (n = 63) canalolithiasis. We analyzed the maximal slow phase velocity (maxSPV), duration, and time constant (Tc) of positional nystagmus, and compared the measures between groups with and without SRPN. We also compared the treatment outcome between two groups. Results: The frequency of SRPN in PC- and HC-BPPV was 47 and 68%, respectively. The maxSPVs were greater in BPPV with SRPN than without, larger in HC-BPPV than PC-BPPV (114.3 ± 56.8 vs. 57.1 ± 38.1°/s, p < 0.001). The reversed nystagmus last longer in HC-BPPV than PC-BPPV. The Tc of positional nystagmus got shorter in PC-BPPV with SRPN (3.7 ± 1.8 s) than without SRPN (4.5 ± 2.0 s, p = 0.034), while it was longer during contralesional head turning in HC-BPPV with SRPN (14.8 ± 7.5 s) than that of ipsilesional side (7.3 ±2.8 s, p < 0.001). The treatment response did not significantly differ between groups with and without SRPN in both PC- and HC-BPPV (p = 0.378 and p = 0.737, respectively). Conclusion: The SRPN is common in both PC- and HC-BPPV canalolithiasis. The intensity of rotational stimuli may be a major determinant for the development of short-term central adaptation which utilizes the velocity-storage system below a certain velocity limit. The presence of SRPN is not related to treatment outcome in BPPV.
Keywords: adaptation; benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; nystagmus; spontaneous reversal; velocity storage system.
Copyright © 2020 Choi, Lee, Oh, Choi and Choi.
Figures


References
-
- Mcclure JA. Horizontal canal Bpv. J Otolaryngol. (1985) 14:30–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

