Microbial Degradation and Valorization of Plastic Wastes
- PMID: 32373075
- PMCID: PMC7186362
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00442
Microbial Degradation and Valorization of Plastic Wastes
Abstract
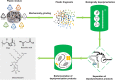
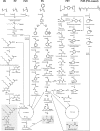
A growing accumulation of plastic wastes has become a severe environmental and social issue. It is urgent to develop innovative approaches for the disposal of plastic wastes. In recent years, reports on biodegradation of synthetic plastics by microorganisms or enzymes have sprung up, and these offer a possibility to develop biological treatment technology for plastic wastes. In this review, we have comprehensively summarized the microorganisms and enzymes that are able to degrade a variety of generally used synthetic plastics, such as polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyurethane (PUR), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). In addition, we have highlighted the microbial metabolic pathways for plastic depolymerization products and the current attempts toward utilization of such products as feedstocks for microbial production of chemicals with high value. Taken together, these findings will contribute to building a conception of bio-upcycling plastic wastes by connecting the biodegradation of plastic wastes to the biosynthesis of valuable chemicals in microorganisms. Last, but not least, we have discussed the challenges toward microbial degradation and valorization of plastic wastes.
Keywords: biodegradation; depolymerase; plastic wastes; protein engineering; synthetic biology; valorization.
Copyright © 2020 Ru, Huo and Yang.
Figures
References
-
- Aguado R., Olazar M., San José M. J., Gaisán B., Bilbao J. (2002). Wax formation in the pyrolysis of polyolefins in a conical spouted bed reactor. Energ. Fuel. 16 1429–1437. 10.1021/ef020043w - DOI
-
- Alariqi S. A., Kumar A. P., Rao B. S. M., Singh R. P. (2006). Biodegradation of γ-sterilised biomedical polyolefins under composting and fungal culture environments. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 91 1105–1116. 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2005.07.004 - DOI
-
- Albertsson A. C. (1978). Biodegradation of synthetic polymers. II. A limited microbial conversion of 14C in polyethylene to 14CO2 by some soil fungi. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 22 3419–3433. 10.1002/app.1978.070221207 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

