A Novel Rapid Sample Preparation Method for MALDI-TOF MS Permits Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato Species and Isolate Differentiation
- PMID: 32373099
- PMCID: PMC7186393
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00690
A Novel Rapid Sample Preparation Method for MALDI-TOF MS Permits Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato Species and Isolate Differentiation
Abstract
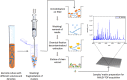
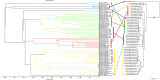
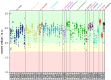
The genus Borrelia comprises vector-borne bacterial pathogens that can severely affect human and animal health. Members of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species complex can cause Lyme borreliosis, one of the most common vector-borne diseases in the Northern hemisphere. Besides, members of the relapsing fever group of spirochetes can cause tick-borne relapsing fever in humans and various febrile illnesses in animals in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions. Borrelia spp. organisms are fastidious to cultivate and to maintain in vitro, and therefore, difficult to work with in the laboratory. Currently, borrelia identification is mainly performed using PCR and DNA sequencing methods, which can be complicated/frustrating on complex DNA templates and may still be relatively expensive. Alternative techniques such as matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) are not well established for Borrelia spp., although this technique is currently one of the most used techniques for rapid identification of bacteria in microbiological diagnostic laboratories. This is mainly due to unsatisfactory results obtained by use of simple sample preparation techniques and medium-contamination obscuring the mass spectra. In addition, comprehensive libraries for Borrelia spp. MALDI-TOF MS have yet to be established. In this study, we developed a new filter-based chemical extraction technique that allows measurement of high quality Borrelia spp. spectra from less than 100,000 bacteria per spot in MALDI-TOF MS. We used 49 isolates of 13 different species to produce the largest mass-library for Borrelia spp. so far and to validate the protocol. The library was successfully established and identifies >96% of used isolates correctly to species level. Cluster analysis on the sum spectra was applied to all the different isolates, which resulted in tight cluster generation for most species. Comparative analysis of the generated cluster to a phylogeny based on concatenated multi-locus sequence typing genes provided a surprising homology. Our data demonstrate that the technique described here can be used for fast and reliable species and strain typing within the borrelia complex.
Keywords: Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato; MALDI-TOF MS; MALDI-TOF MS library; automatic identification; sample preparation; strain typing; typing.
Copyright © 2020 Neumann-Cip, Fingerle, Margos, Straubinger, Overzier, Ulrich and Wieser.
Figures

References
-
- Caimano M. J., Groshong A. M., Belperron A., Mao J., Hawley K. L., Luthra A., et al. (2019). The RpoS Gatekeeper in Borrelia burgdorferi: An Invariant Regulatory Scheme That Promotes Spirochete Persistence in Reservoir Hosts and Niche Diversity. Frontiers in Microbiology 10:1923. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01923 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

