Calculated parenteral initial therapy of bacterial infections: Bacterial meningitis
- PMID: 32373432
- PMCID: PMC7186794
- DOI: 10.3205/id000051
Calculated parenteral initial therapy of bacterial infections: Bacterial meningitis
Abstract
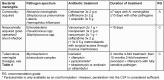
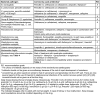
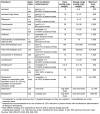
This is the thirteenth chapter of the guideline "Calculated initial parenteral treatment of bacterial infections in adults - update 2018" in the 2nd updated version. The German guideline by the Paul-Ehrlich-Gesellschaft für Chemotherapie e.V. (PEG) has been translated to address an international audience. Bacterial meningitis is a life-threatening infectious disease with high mortality and disability rates requiring prompt initiation of antimicrobial treatment to lower these rates.
Dies ist das 13. Kapitel der von der Paul-Ehrlich-Gesellschaft für Chemotherapie e.V. (PEG) herausgegebenen S2k Leitlinie „Kalkulierte parenterale Initialtherapie bakterieller Erkrankungen bei Erwachsenen – Update 2018“ in der 2. aktualisierten Fassung.Die bakterielle Meningitis ist eine lebensbedrohliche Infektionskrankheit mit hohen Mortalitäts- und Invaliditätsraten, die den sofortigen Beginn einer antimikrobiellen Behandlung erfordert, um diese Raten zu senken.
Copyright © 2020 Shah et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bohr V, Hansen B, Jessen O, Johnsen N, Kjersem H, Kristensen HS, Nyboe J, Rasmussen N. Eight hundred and seventy-five cases of bacterial meningitis. Part I of a three-part series: clinical data, prognosis, and the role of specialised hospital departments. J Infect. 1983 Jul;7(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/S0163-4453(83)90894-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Robert Koch Institut. Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2014. Berlin: RKI; 2015. - DOI
-
- Reiber H, Lange P. Quantification of virus-specific antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid and serum: sensitive and specific detection of antibody synthesis in brain. Clin Chem. 1991 Jul;37(7):1153–1160. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
