Calculated parenteral initial treatment of bacterial infections: Intra-abdominal infections
- PMID: 32373438
- PMCID: PMC7186812
- DOI: 10.3205/id000057
Calculated parenteral initial treatment of bacterial infections: Intra-abdominal infections
Abstract
This is the seventh chapter of the guideline "Calculated initial parenteral treatment of bacterial infections in adults - update 2018" in the 2nd updated version. The German guideline by the Paul-Ehrlich-Gesellschaft für Chemotherapie e.V. (PEG) has been translated to address an international audience. The chapter deals with the empirical and targeted antimicrobial therapy of complicated intra-abdominal infections. It includes recommendations for antibacterial and antifungal treatment.
Dies ist das siebte Kapitel der von der Paul-Ehrlich-Gesellschaft für Chemotherapie e.V. (PEG) herausgegebenen S2k Leitlinie „Kalkulierte parenterale Initialtherapie bakterieller Erkrankungen bei Erwachsenen – Update 2018“ in der 2. aktualisierten Fassung.Es behandelt die empirische und gezielte antimikrobielle Therapie komplizierter intraabdominaler Infektionen und enthält Empfehlungen für die antibakterielle und antimykotische Behandlung.
Copyright © 2020 Eckmann et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

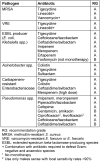



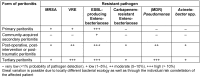
References
-
- Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, Light B, Parrillo JE, Sharma S, Suppes R, Feinstein D, Zanotti S, Taiberg L, Gurka D, Kumar A, Cheang M. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2006 Jun;34(6):1589–1596. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000217961.75225.E9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Engel C, Brunkhorst FM, Bone HG, Brunkhorst R, Gerlach H, Grond S, Gruendling M, Huhle G, Jaschinski U, John S, Mayer K, Oppert M, Olthoff D, Quintel M, Ragaller M, Rossaint R, Stuber F, Weiler N, Welte T, Bogatsch H, Hartog C, Loeffler M, Reinhart K. Epidemiology of sepsis in Germany: results from a national prospective multicenter study. Intensive Care Med. 2007 Apr;33(4):606–618. doi: 10.1007/s00134-006-0517-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
