Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Groundbreaking Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery
- PMID: 32373485
- PMCID: PMC7191226
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2020.021
Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Groundbreaking Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery
Abstract
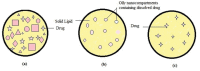
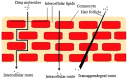
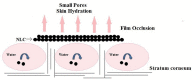
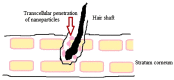
Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) are novel pharmaceutical formulations which are composed of physiological and biocompatible lipids, surfactants and co-surfactants. Over time, as a second generation lipid nanocarrier NLC has emerged as an alternative to first generation nanoparticles. This review article highlights the structure, composition, various formulation methodologies, and characterization of NLCs which are prerequisites in formulating a stable drug delivery system. NLCs hold an eminent potential in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics market because of extensive beneficial effects like skin hydration, occlusion, enhanced bioavailability, and skin targeting. This article aims to evoke an interest in the current state of art NLC by discussing their promising assistance in topical drug delivery system. The key attributes of NLC that make them a promising drug delivery system are ease of preparation, biocompatibility, the feasibility of scale up, non-toxicity, improved drug loading, and stability.
Keywords: Lipid; Nanostructure lipid carrier; Skin; Topical.
© 2020 The Authors.
Similar articles
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic dermal products.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007 Jul 10;59(6):522-30. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.04.012. Epub 2007 May 17. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007. PMID: 17602783
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers for site-specific drug delivery.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jul;103:598-613. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.055. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29677547 Review.
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers as semisolid topical delivery formulations for diflucortolone valerate.J Liposome Res. 2017 Mar;27(1):41-55. doi: 10.3109/08982104.2016.1149866. Epub 2016 Mar 9. J Liposome Res. 2017. PMID: 26956098
-
Enhanced transdermal delivery of lornoxicam by nanostructured lipid carrier gels modified with polyarginine peptide for treatment of carrageenan-induced rat paw edema.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Aug 2;14:6135-6150. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S205295. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31447556 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructured lipid (NLCs) carriers as a bioavailability enhancement tool for oral administration.Drug Deliv. 2015;22(6):691-700. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.898110. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24670099 Review.
Cited by
-
Penetration study of p-methoxycinnamic acid (PMCA) in nanostructured lipid carrier, solid lipid nanoparticles, and simple cream into the rat skin.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 12;12(1):19365. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23514-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36371457 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial Delivery of Docetaxel- and Erlotinib-Loaded Functionalized Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Using Quality-by-Design Approach.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 11;16(7):926. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070926. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065626 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Nanotechnological Advancements of Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs into Rheumatoid Arthritis Management.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 14;17(2):248. doi: 10.3390/ph17020248. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing hair regeneration: Recent progress in tailoring nanostructured lipid carriers through surface modification strategies.ADMET DMPK. 2024 Jul 20;12(3):431-462. doi: 10.5599/admet.2376. eCollection 2024. ADMET DMPK. 2024. PMID: 39091900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-Therapeutics to Treat Acne Vulgaris.Indian J Microbiol. 2022 Jun;62(2):167-174. doi: 10.1007/s12088-022-01001-4. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Indian J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35462720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- López-García R, Ganem-Rondero A. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): Occlusive Effect and Penetration Enhancement Ability. J Cosmet Dermatol Sci Appl. 2015;5(2):62–72. doi: 10.4236/jcdsa.2015.52008. - DOI
-
- Jain P, Rahi P, Pandey V, Asati S, Soni V. Nanostructure lipid carriers: a modish contrivance to overcome the ultraviolet effects. Egypt J Basic Appl Sci. 2017;4(2):89–100. doi: 10.1016/j.ejbas.2017.02.001. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources